Publication date: May–June 2018
Source:Allergologia et Immunopathologia, Volume 46, Issue 3
Author(s): L. Garcia-Marcos
https://ift.tt/2GDsAkQ
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2020
(289)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
►
2019
(9071)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (3642)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (3200)
-
▼
2018
(39872)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3318)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (3683)
-
▼
Απριλίου
(3319)
-
▼
Απρ 05
(88)
- Wheezing in infants: A pandemic condition that nee...
- A Role for Satb1 in Thyroid Autoimmunity?
- An Online Survey of Hypothyroid Patients Demonstra...
- Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome (FPIES...
- Comparison of Two Protocols of Misoprostol (PGE1) ...
- Remote Activity Monitored by Fitbit Charge 2 in In...
- Assessment of Histopathological Grade and Ki-67 Ex...
- Benralizumab efficacy by atopy status and serum im...
- Transcription and microRNA Profiling of Cultured H...
- Moving beyond surveys to assess patient preferences
- Facial nerve palsy and laryngospasm as a complicat...
- In whom does horizontal canal BPPV recur?
- Effect of changing postoperative pain management o...
- Prognostic Implication of N1b Classification in th...
- Association Between Thyroid Function and Developme...
- NIH completes in-depth genomic analysis of 33 canc...
- Treatment of T3 Glottic Cancer
- Survival Outcomes for Patients With T3N0M0 Squamou...
- A Child’s Complaint of “Throat Freeze”—Not Brain F...
- Thyroidosis Mistaken for Thyroid Cancer
- Life Experience of Patients With Unilateral Vocal ...
- Auricular Swelling After Mild Trauma
- An Atypical Case of Bartonella henselae Osteomyeli...
- How do you prevent pimples?
- The Role of Localized Compressional Ultra-low Freq...
- Upscaling Participatory Action and Videos for Agri...
- Verbal learning and hippocampal dysfunction in sch...
- Rare variant analysis in multiply affected familie...
- Mendelian adult-onset leukodystrophy genes in Alzh...
- World TB Day 2018: The Challenge of Drug Resistant...
- Repellent and Attractant Guidance Cues Initiate Ce...
- Multiple roles of Sonic Hedgehog in the developing...
- Stability-based multivariate mapping using SCoRS
- Proteomic identification and characterization of h...
- The fiscal theory of the price level in a world of...
- Non-PTLD Malignancy post HSCT in patients with Pri...
- Coherent Spin Amplification Using a Beam Splitter
- Accommodating informative dropout and death: a joi...
- Sexualities and queer migration research
- Accurate prediction of X-ray pulse properties from...
- Power and sample-size analysis for the Royston–Par...
- Risk preference and choice stochasticity during de...
- Blended diets for gastrostomy fed children and you...
- Eestlastest sõjavangide erikohtlemispoliitika Esim...
- To Track Environmental Impact On Genome, Don’t For...
- Presence of hepatitis B surface antibody in additi...
- Prediction of the Development of Persistent Massiv...
- Immune-mediated cholangitis: is it always nivoluma...
- Aripiprazole-induced sleep-related eating disorder...
- Animal Study Suggests Common Diabetes Drug May Als...
- Severe inflammatory ileitis resulting in ileal per...
- More than meets the eye: infant presenting with hy...
- Paediatric non-ketotic hyperglycaemic hemichorea-h...
- Mucinous adenocarcinoma arising from chronic peria...
- Klebsiella endophthalmitis as the herald of occult...
- Native valve endocarditis, fusarium and end-stage ...
- Epidermoid cyst within an intrapancreatic accessor...
- Infectious causes of Addisons disease: 1 organ--2 ...
- Uncommon presentation, rare complication and previ...
- Varicella-zoster virus necrotising retinitis, reti...
- Isolated cystic lymphangiomatosis of spleen in an ...
- Hypocalcaemia in an adult: the importance of not o...
- Chiari malformation and tuberculous meningitis: ae...
- Bilateral multifocal acute lobar nephronia caused ...
- Scorpion bite-induced unilateral pulmonary oedema
- Rapunzel syndrome: a tail too long to tell!
- Immune stromal keratitis: a rare ocular presentati...
- Perforated gastric remnant ulcer after laparoscopi...
- Health professionals' and coroners' views on less ...
- Alveolar T-helper 17 responses to streptococcus pn...
- Beyond Jam Sandwiches and Cups of Tea: An Explorat...
- Identification of neural structures involved in st...
- Immunosuppressive agents in adult kidney transplan...
- Risk factors for salivary gland cancers in France:...
- Hypoxia modulates CCR7 expression in head and neck...
- Multi-criteria optimization achieves superior norm...
- A predictive model for recurrence in patients with...
- The clinical outcome and microbiological profile o...
- Stream of Consciousness
- Vaccination against IL-31 for the treatment of ato...
- Th1/Th17 cell recognition of desmoglein 3 and bull...
- Correlation of allergen-specific T follicular help...
- Obesity and asthma
- Treating insect-bite hypersensitivity in horses wi...
- Obesity and asthma
- The Editors' Choice
- News Beyond Our Pages
- Role of the Microbiome in Food Allergy
-
▼
Απρ 05
(88)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (2693)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (3198)
-
►
2017
(41099)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3127)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (2173)
-
►
2016
(13807)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (700)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (600)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (1350)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (1400)
-
►
2015
(1500)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (1450)
Ετικέτες
Πέμπτη 5 Απριλίου 2018
Wheezing in infants: A pandemic condition that need to be treated with patience
A Role for Satb1 in Thyroid Autoimmunity?
Thyroid, Ahead of Print.
https://ift.tt/2qaPjxx
An Online Survey of Hypothyroid Patients Demonstrates Prominent Dissatisfaction
Thyroid, Ahead of Print.
https://ift.tt/2GDpT6U
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome (FPIES): Review of Recent Guidelines
Abstract
Purpose of Review
To increase understanding of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome (FPIES), a non-immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated reaction to food, by reviewing a growing body of literature, including recently published international consensus guidelines.
Recent Findings
FPIES primarily affects infants and young children and is characterized by the delayed onset of gastrointestinal symptoms, predominantly repetitive vomiting, in response to a trigger food. Symptoms are often severe and can lead to shock. Diagnosis can be challenging due to a wide differential diagnoses and lack of disease biomarkers. FPIES is a clinical diagnosis, with allergy testing playing a very limited role, if any. Medically supervised oral food challenges are used to monitor resolution of disease, which generally occurs in early childhood.
Summary
FPIES is an important condition presenting to clinicians in a variety of settings. Recent international consensus guidelines and a growing body of literature can better equip practitioners to care for these often-challenging patients.
https://ift.tt/2uOOUGG
Comparison of Two Protocols of Misoprostol (PGE1) and the Rate of Cesarean Section Due to Failed Induction.
Interventions: Procedure: 6 misoprostol; Procedure: 3 misoprostol
Sponsors: Saint Thomas Hospital, Panama; Sistema Nacional de Investigadores de Panamá
Not yet recruiting
https://ift.tt/2JoUqmM
Remote Activity Monitored by Fitbit Charge 2 in Investigating Daily Step and Sleep Data in Participants With Head and Neck Cancer Undergoing Radiation Therapy
Intervention: Device: Monitoring Device
Sponsor: Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center at Thomas Jefferson University
Not yet recruiting
https://ift.tt/2Ix9Mo4
Assessment of Histopathological Grade and Ki-67 Expression in Tobacco and Non-tobacco Habitual Buccal Mucosa Cancer
Abstract
Although there are various risk factors in the literature, the established primary risk factor for oral cancer is tobacco and betal-nut chewing habits. It is believed that pathogenesis of oral cancer depends on the aetiology. To assess the histopathological grade and Ki-67 expression in tobacco (smoking/smokeless) and non-tobacco (betal nut/pan masala) habitual buccal mucosa cancer. The cross-sectional study was carried out in Regional cancer centre, Tamilnadu. Proliferative marker, Ki-67 expression was determined by immunohistochemistry using biotin-streptavidin method. The study includes 117 buccal mucosa cancer patients (61 male and 56 female). According to WHO grading system, high frequency observed with well differentiated squamous cell carcinoma 48 (41%) followed by moderate 46 (39.3%) and poorly differentiated 23 (19.7%). The cut-off value 50% was used to categorize Ki-67 expression into low and high labelling index (LI); 96 (82%) buccal mucosa cancer and 4 (3.4%) adjacent normal mucosa patients showed high Ki-67 expression. The present study showed highly significant association of histopathological tumor grade and Ki-67 expression by Chi square and paired t test p < 0.05. All the patients were grouped as tobacco 87 (74.4%) and non-tobacco habitual 30 (25.6%) in 3:1, respectively. Further, the risk habits identified with significant differences of tumor grade (p = 0.028) and Ki-67 at p < 0.05. Thus, the study revealed that the nature of cell differentiation and proliferation was strongly related to consumption of carcinogen in both tobacco and non-tobacco form. Therefore, histopathological grade and Ki-67 could be used as a reliable biomarker to understand the biological behaviour of risk habits which might helpful for further treatment therapeutics.
https://ift.tt/2EkJeUx
Benralizumab efficacy by atopy status and serum immunoglobulin E for patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma
Patients with severe asthma can have eosinophilic inflammation and/or allergen sensitization. Benralizumab is an anti-eosinophilic monoclonal antibody being developed for patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma with eosinophilic inflammation.
https://ift.tt/2ItKvv2
Transcription and microRNA Profiling of Cultured Human Tympanic Membrane Epidermal Keratinocytes
Abstract
The human tympanic membrane (TM) has a thin outer epidermal layer which plays an important role in TM homeostasis and ear health. The specialised cells of the TM epidermis have a different physiology compared to normal skin epidermal keratinocytes, displaying a dynamic and constitutive migration that maintains a clear TM surface and assists in regeneration. Here, we characterise and compare molecular phenotypes in keratinocyte cultures from TM and normal skin. TM keratinocytes were isolated by enzymatic digestion and cultured in vitro. We compared global mRNA and microRNA expression of the cultured cells with that of human epidermal keratinocyte cultures. Genes with either relatively higher or lower expression were analysed further using the biostatistical tools g:Profiler and Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Approximately 500 genes were found differentially expressed. Gene ontology enrichment and Ingenuity analyses identified cellular migration and closely related biological processes to be the most significant functions of the genes highly expressed in the TM keratinocytes. The genes of low expression showed a marked difference in homeobox (HOX) genes of clusters A and C, giving the TM keratinocytes a strikingly low HOX gene expression profile. An in vitro scratch wound assay showed a more individualised cell movement in cells from the tympanic membrane than normal epidermal keratinocytes. We identified 10 microRNAs with differential expression, several of which can also be linked to regulation of cell migration and expression of HOX genes. Our data provides clues to understanding the specific physiological properties of TM keratinocytes, including candidate genes for constitutive migration, and may thus help focus further research.
https://ift.tt/2H17gco
Facial nerve palsy and laryngospasm as a complication of local anaesthesia during adenotonsillectomy
Tonsil surgeries are the most frequently performed surgical procedures in ENT departments. We would like to present the case of a 5-year-old patient who suffered from unilateral peripheral facial nerve palsy and laryngeal spasm following adenotonsillectomy. Paresis was observed immediately after the transfer of the patient to the postoperative room. The activity of facial muscles was restored within 2 hours from the beginning of the surgery. We assume that this was the direct effect of an anaesthetic on the extracranial processes of the facial nerve.
https://ift.tt/2Iysvzl
In whom does horizontal canal BPPV recur?
![]()
Source:American Journal of Otolaryngology
Author(s): L. Pollak, R. Huna-Baron, Michael Osherov, Milo Roni
PurposeThe objective of this study is to examine the rate of horizontal canal BPPV recurrence of the same type and search for predisposing factors.
https://ift.tt/2Hc4Pl9
Effect of changing postoperative pain management on bleeding rates in tonsillectomy patients
![]()
Source:American Journal of Otolaryngology
Author(s): Alexandra C.G. Fonseca, Margaret I. Engelhardt, Zhen J. Huang, Zi Yang Jiang, Sancak Yuksel, Soham Roy
PurposeTo review rates of post-tonsillectomy hemorrhage (PTH) at a quaternary medical center, including the impact of narcotic versus nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) postoperative pain management.Materials and methodsA retrospective review was performed of tonsillectomies conducted at a single institution between 1/1/2013 and 1/1/2017. The rates of PTH and subsequent intervention were calculated. These were categorized into patients having surgery pre- and post-July 1, 2015, the former group receiving narcotics and the latter ibuprofen with acetaminophen.ResultsOf 1351 total tonsillectomies, 3.04% had PTH requiring return to the hospital. 0.74% required no further surgical intervention, whereas 2.30% required secondary surgical control. The bleed rate prior to July 2015 was 3.15%, with 1.05% non-surgical bleeds and 2.10% requiring surgery. Post-July 2015, the bleed rate was 2.92%, with 0.44% non-surgical bleeds and 2.49% requiring surgery. There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups with respect to overall, non-surgical, and surgical hemorrhage rates (p > 0.05). Of the total bleeds, the need for secondary surgery in the narcotic group was 66.7% and 85% in the NSAID group (p = 0.18). During the study period, 36 patients with PTH had their initial tonsillectomy performed at outside institutions; 53% required surgical intervention.ConclusionsSecondary hemorrhage remains a significant cause of morbidity in post-tonsillectomy patients, often requiring surgical intervention. This review found no increased bleeding risk associated with use of ibuprofen and acetaminophen as opposed to narcotic pain relief.Level of evidence2b
https://ift.tt/2EmNaUH
Prognostic Implication of N1b Classification in the Eighth Edition of the Tumor-Node-Metastasis Staging System of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid, Ahead of Print.
https://ift.tt/2JoOOsu
Association Between Thyroid Function and Development of Different Obesity Phenotypes in Euthyroid Adults: A Nine-Year Follow-Up
Thyroid, Ahead of Print.
https://ift.tt/2Iwj2bV
NIH completes in-depth genomic analysis of 33 cancer types
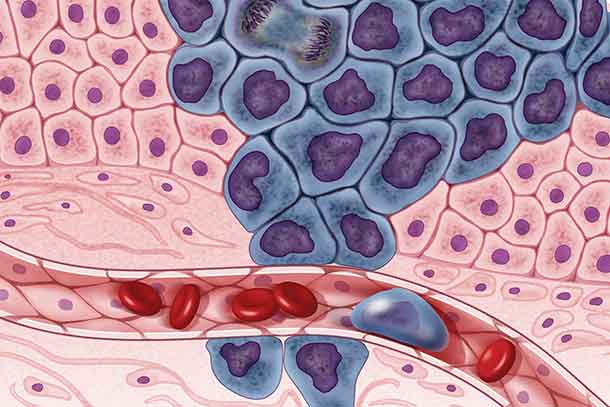
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), supported by NIH's NHGRI and NCI, concludes with an in-depth genomic analysis of 33 cancer types called the PanCancer Atlas. Findings are being published as a collection of 27 papers across multiple Cell journals.
https://ift.tt/2qa4g3K
Treatment of T3 Glottic Cancer
https://ift.tt/2uLJufS
Survival Outcomes for Patients With T3N0M0 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Glottic Larynx—Reply
https://ift.tt/2q7ONl0
A Child’s Complaint of “Throat Freeze”—Not Brain Freeze—and Experiences With Zenker Diverticulum
https://ift.tt/2GB0w1C
Thyroidosis Mistaken for Thyroid Cancer
https://ift.tt/2q9XWtd
Life Experience of Patients With Unilateral Vocal Fold Paralysis
https://ift.tt/2uLjrW1
Auricular Swelling After Mild Trauma
https://ift.tt/2q85Y61
An Atypical Case of Bartonella henselae Osteomyelitis and Hepatic Disease
Bartonella henselae is a Gram-negative bacterium and the causative agent of cat scratch disease (CSD). Atypical presentations of B. henselae that involve the musculoskeletal, hepatosplenic, cardiac, or neurologic systems are rare. In this case report, we describe a case of B. henselae osteomyelitis involving bilateral iliac bones complicated by hepatic lesions in a 12-year-old immunocompetent female patient. Although B. henselae is a rare cause of osteomyelitis, it should be considered when patients who present with fever, pain, and lymphadenopathy do not respond to routine osteomyelitis therapy.
https://ift.tt/2uRCgH4
How do you prevent pimples?
Several factors can cause acne, but simple hygiene techniques and lifestyle changes can often prevent pimples from forming. Washing regularly and reducing stress are some of the best ways to ward off this common skin issue. Here, learn more about effective methods of prevention and treatment.
https://ift.tt/2HaQ6Xs
The Role of Localized Compressional Ultra-low Frequency Waves in Energetic Electron Precipitation
Jonathan Rae, I; Murphy, KR; Watt, CEJ; Halford, AJ; Mann, IR; Ozeke, LG; Sibeck, DG; ... Singer, HJ; + view all Jonathan Rae, I; Murphy, KR; Watt, CEJ; Halford, AJ; Mann, IR; Ozeke, LG; Sibeck, DG; Clilverd, MA; Rodger, CJ; Degeling, AW; Forsyth, C; Singer, HJ; - view fewer (2018) The Role of Localized Compressional Ultra-low Frequency Waves in Energetic Electron Precipitation. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics 10.1002/2017JA024674 . (In press). Green open access
https://ift.tt/2JmiUNB
Upscaling Participatory Action and Videos for Agriculture and Nutrition (UPAVAN) trial comparing three variants of a nutrition-sensitive agricultural extension intervention to improve maternal and child nutritional outcomes in rural Odisha, India: study protocol for a cluster randomised controlled trial
Kadiyala, S; Prost, A; Harris-Fry, H; O'Hearn, M; Pradhan, R; Pradhan, S; Mishra, NK; ... Allen, E; + view all Kadiyala, S; Prost, A; Harris-Fry, H; O'Hearn, M; Pradhan, R; Pradhan, S; Mishra, NK; Rath, S; Nair, N; Rath, S; Tripathy, P; Krishnan, S; Koniz-Booher, P; Danton, H; Elbourne, D; Sturgess, J; Beaumont, E; Haghparast-Bidgoli, H; Skordis-Worrall, J; Mohanty, S; Upadhay, A; Allen, E; - view fewer (2018) Upscaling Participatory Action and Videos for Agriculture and Nutrition (UPAVAN) trial comparing three variants of a nutrition-sensitive agricultural extension intervention to improve maternal and child nutritional outcomes in rural Odisha, India: study protocol for a cluster randomised controlled trial. Trials , 19 , Article 176. 10.1186/s13063-018-2521-y . Green open access
https://ift.tt/2uN6LOl
Verbal learning and hippocampal dysfunction in schizophrenia: A meta analysis
Antoniades, M; Schoeler, T; Radua, J; Valli, I; Allen, P; Kempton, MJ; McGuire, P; (2017) Verbal learning and hippocampal dysfunction in schizophrenia: A meta analysis. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews , 86 pp. 166-175. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.12.001 . Green open access
https://ift.tt/2Jl8GwP
Rare variant analysis in multiply affected families, association studies and functional analysis suggest a role for the ITGΒ4 gene in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder
O'Brien, NL; Fiorentino, A; Curtis, D; Rayner, C; Petrosellini, C; Al Eissa, M; Bass, NJ; ... Sharp, SI; + view all O'Brien, NL; Fiorentino, A; Curtis, D; Rayner, C; Petrosellini, C; Al Eissa, M; Bass, NJ; McQuillin, A; Sharp, SI; - view fewer (2018) Rare variant analysis in multiply affected families, association studies and functional analysis suggest a role for the ITGΒ4 gene in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophrenia Research 10.1016/j.schres.2018.03.001 . (In press). Green open access
https://ift.tt/2IuP7kh
Mendelian adult-onset leukodystrophy genes in Alzheimer's disease: critical influence of CSF1R and NOTCH3
Sassi, C; Nalls, MA; Ridge, PG; Gibbs, JR; Lupton, MK; Troakes, C; Lunnon, K; ... Hardy, J; + view all Sassi, C; Nalls, MA; Ridge, PG; Gibbs, JR; Lupton, MK; Troakes, C; Lunnon, K; Al-Sarraj, S; Brown, KS; Medway, C; Lord, J; Turton, J; Bras, J; ARUK Consortium, ; Blumenau, S; Thielke, M; Josties, C; Freyer, D; Dietrich, A; Hammer, M; Baier, M; Dirnagl, U; Morgan, K; Powell, JF; Kauwe, JS; Cruchaga, C; Goate, AM; Singleton, AB; Guerreiro, R; Hodges, A; Hardy, J; - view fewer (2018) Mendelian adult-onset leukodystrophy genes in Alzheimer's disease: critical influence of CSF1R and NOTCH3. Neurobiology Aging 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.01.015 . Green open access
https://ift.tt/2JneJko
World TB Day 2018: The Challenge of Drug Resistant Tuberculosis.
Gupta-Wright, A; Tomlinson, GS; Rangaka, MX; Fletcher, HA; (2018) World TB Day 2018: The Challenge of Drug Resistant Tuberculosis. [Editorial comment]. F1000Res , 7 p. 217. 10.12688/f1000research.14088.1 . Green open access
https://ift.tt/2uOGVcD
Repellent and Attractant Guidance Cues Initiate Cell Migration by Distinct Rear-Driven and Front-Driven Cytoskeletal Mechanisms.
Cramer, LP; Kay, RR; Zatulovskiy, E; (2018) Repellent and Attractant Guidance Cues Initiate Cell Migration by Distinct Rear-Driven and Front-Driven Cytoskeletal Mechanisms. Curr Biol , 28 (6) 995-1004.e3. 10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.024 . Green open access
https://ift.tt/2uO5RRJ
Multiple roles of Sonic Hedgehog in the developing human cortex are suggested by its widespread distribution
Memi, F; Zecevic, N; Radonjić, N; (2018) Multiple roles of Sonic Hedgehog in the developing human cortex are suggested by its widespread distribution. Brain Structure and Function 10.1007/s00429-018-1621-5 . (In press). Green open access
https://ift.tt/2JmBB3M
Stability-based multivariate mapping using SCoRS
Rondina, JM; Shawe-Taylor, J; Mourao-Miranda, J; (2013) Stability-based multivariate mapping using SCoRS. In: Davatzikos, C, (ed.) 3rd International Workshop on Pattern Recognition in Neuroimaging (PRNI 2013): Proceedings. (pp. pp. 198-202). IEEE Green open access
https://ift.tt/2JmQEua
Proteomic identification and characterization of hepatic glyoxalase 1 dysregulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Spanos, C; Maldonado, EM; Fisher, CP; Leenutaphong, P; Oviedo-Orta, E; Windridge, D; Salguero, FJ; ... Moore, JB; + view all Spanos, C; Maldonado, EM; Fisher, CP; Leenutaphong, P; Oviedo-Orta, E; Windridge, D; Salguero, FJ; Bermudez-Fajardo, A; Weeks, ME; Evans, C; Corfe, BM; Rabbani, N; Thornalley, PJ; Miller, MH; Wang, H; Dillon, JF; Quaglia, A; Dhawan, A; Fitzpatrick, E; Moore, JB; - view fewer (2018) Proteomic identification and characterization of hepatic glyoxalase 1 dysregulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Proteome Science , 16 , Article 4. 10.1186/s12953-018-0131-y . Green open access
https://ift.tt/2uO5Flt
The fiscal theory of the price level in a world of low interest rates
Bassetto, M; Cui, W; (2018) The fiscal theory of the price level in a world of low interest rates. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control , 89 pp. 5-22. 10.1016/j.jedc.2018.01.006 .
https://ift.tt/2Jo1Oib
Non-PTLD Malignancy post HSCT in patients with Primary Immunodeficiency: UK experience
Unni, MNM; Elfeky, R; Rao, K; Nademi, Z; Chiesa, R; Amrolia, P; Skinner, R; ... Slatter, MA; + view all Unni, MNM; Elfeky, R; Rao, K; Nademi, Z; Chiesa, R; Amrolia, P; Skinner, R; Slater, O; Worth, A; Flood, T; Abinun, M; Hambleton, S; Qasim, W; Gaspar, HB; Cant, AJ; Gennery, AR; Veys, P; Slatter, MA; - view fewer (2018) Non-PTLD Malignancy post HSCT in patients with Primary Immunodeficiency: UK experience. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.02.038 .
https://ift.tt/2Iry5n6
Coherent Spin Amplification Using a Beam Splitter
Yan, C; KUMAR, S; Thomas, K; See, P; Farrer, I; Ritchie, D; Griffiths, J; ... Pepper, M; + view all Yan, C; KUMAR, S; Thomas, K; See, P; Farrer, I; Ritchie, D; Griffiths, J; Jones, G; Pepper, M; - view fewer (2018) Coherent Spin Amplification Using a Beam Splitter. Physical Review Letters , 120 (13) , Article 137701. 10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.137701 . Green open access
https://ift.tt/2HaemJj
Accommodating informative dropout and death: a joint modelling approach for longitudinal and semicompeting risks data
Li, Q; Su, L; (2018) Accommodating informative dropout and death: a joint modelling approach for longitudinal and semicompeting risks data. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series C (Applied Statistics) , 67 (1) pp. 145-163. 10.1111/rssc.12210 . Green open access
https://ift.tt/2uOGTBx
Sexualities and queer migration research
Mole, RCM; (2018) Sexualities and queer migration research. Sexualities (In press).
https://ift.tt/2Jo1n7x
Accurate prediction of X-ray pulse properties from a free-electron laser using machine learning
Sanchez-Gonzalez, A; Micaelli, P; Olivier, C; Barillot, TR; Ilchen, M; Lutman, AA; Marinelli, A; ... Marangos, JP; + view all Sanchez-Gonzalez, A; Micaelli, P; Olivier, C; Barillot, TR; Ilchen, M; Lutman, AA; Marinelli, A; Maxwell, T; Achner, A; Agåker, M; Berrah, N; Bostedt, C; Bozek, JD; Buck, J; Bucksbaum, PH; Montero, SC; Cooper, B; Cryan, JP; Dong, M; Feifel, R; Frasinski, LJ; Fukuzawa, H; Galler, A; Hartmann, G; Hartmann, N; Helml, W; Johnson, AS; Knie, A; Lindahl, AO; Liu, J; Motomura, K; Mucke, M; O'Grady, C; Rubensson, JE; Simpson, ER; Squibb, RJ; Såthe, C; Ueda, K; Vacher, M; Walke, DJ; Zhaunerchyk, V; Coffee, RN; Marangos, JP; - view fewer (2017) Accurate prediction of X-ray pulse properties from a free-electron laser using machine learning. Nature Communications , 8 , Article 15461. 10.1038/ncomms15461 . Green open access
https://ift.tt/2uTWFuW
Power and sample-size analysis for the Royston–Parmar combined test in clinical trials with a time-to-event outcome
Royston, P; (2018) Power and sample-size analysis for the Royston–Parmar combined test in clinical trials with a time-to-event outcome. Stata Journal , 18 (1) pp. 3-21. Green open access
https://ift.tt/2HbNwQV
Risk preference and choice stochasticity during decisions for other people
Rigoli, F; Preller, KH; Dolan, RJ; (2018) Risk preference and choice stochasticity during decisions for other people. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience 10.3758/s13415-018-0572-x . (In press). Green open access
https://ift.tt/2uJPaqo
Blended diets for gastrostomy fed children and young people: A scoping review
Breaks, A; Sally, M; Smith, CH; Bloch, SJ; (2018) Blended diets for gastrostomy fed children and young people: A scoping review. Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics (In press).
https://ift.tt/2JlAPUx
Eestlastest sõjavangide erikohtlemispoliitika Esimese maailmasõja aegsel Saksamaal
Kuldkepp, M; (2018) Eestlastest sõjavangide erikohtlemispoliitika Esimese maailmasõja aegsel Saksamaal. Tuna. Ajalookultuuri ajakiri (4) (In press).
https://ift.tt/2uJOOQA
To Track Environmental Impact On Genome, Don’t Forget The “epi” In Genetics Research, Johns Hopkins Scientist Says

In a review article published April 5 in the New England Journal of Medicine, scientist Andrew Feinberg, M.D., calls for more integration between two fields of DNA-based research: genetics and epigenetics.
https://ift.tt/2Elolsp
Presence of hepatitis B surface antibody in addition to hepatitis B core antibody confers protection against hepatitis B virus infection in hepatitis B surface antigen–negative patients undergoing kidney transplantation
https://ift.tt/2q7r3NU
Prediction of the Development of Persistent Massive Ascites after Living Donor Liver Transplantation Using a Perioperative Risk Score
https://ift.tt/2uTTqUi
Aripiprazole-induced sleep-related eating disorder: a case report
Sleep-related eating disorder is characterized by parasomnia with recurrent episodes of nocturnal eating or drinking during the main sleep period. Several drugs, including atypical antipsychotics, induce sleep...
https://ift.tt/2HaDX4O
Animal Study Suggests Common Diabetes Drug May Also Help with Nicotine Withdrawal

In a mouse study, a drug that has helped millions of people around the world manage their diabetes might also help people ready to kick their nicotine habits.
https://ift.tt/2Elf0AR
Severe inflammatory ileitis resulting in ileal perforation in association with combination immune checkpoint blockade for metastatic malignant melanoma
Immune checkpoint inhibitors have become standard of care in metastatic malignant melanoma management. Despite superior effectiveness to chemotherapy, significant immune-related adverse events (irAE) may occur, particularly if used in combination. Gastrointestinal irAEs were reported with different patterns of involvement. Here, we report the case of a patient who had ileal perforation as a complication of terminal ileitis, without colitis, induced by combination immune checkpoint blockade.
https://ift.tt/2q91RWu
More than meets the eye: infant presenting with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy
We report a newborn infant who presented with poor Apgar scores and umbilical artery acidosis leading to the diagnosis of hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. During the course of the infant's hospitalisation, subsequent workup revealed an underlying genetic cause that masqueraded as hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy.
https://ift.tt/2JmmzLo
Paediatric non-ketotic hyperglycaemic hemichorea-hemiballismus
Non-ketotic hyperglycaemic hemichorea–hemiballismus (NHHH) is commonly seen among elderly Asian women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Here, we present a case of a 16-year-old Filipina with type 1 diabetes mellitus who is poorly compliant to her medications and subsequently developed right hemichorea–hemiballismus (HH). She was initially admitted with hyperglycaemia but was negative for ketonuria or metabolic acidosis. Neuroimaging showed bilateral lentiform nuclei and left caudate hyperdensities on CT and T1-weighted hyperintensity on MRI. Blood glucose was controlled with insulin. Haloperidol and clonazepam were started for the HH with gradual resolution of symptoms in 6 weeks. This is the fifth reported case of NHHH seen among the paediatric age group. NHHH in the paediatric population is clinically and radiographically similar to NHHH seen among adults. Correction of hyperglycaemia results in clinical improvement and radiographic resolution of lesions but persistent cases may necessitate specific treatment targeted towards the abnormal movements.
https://ift.tt/2qd6IWL
Mucinous adenocarcinoma arising from chronic perianal fistula mimicking horseshoe abscess
Perianal fistulae are commonly seen clinical entity. Development of malignancy within a perianal fistula is rare. Even rarer is the development of mucinous adenocarcinoma in a chronic fistula-in-ano. Only a handful of such cases have been reported in the past. A case of mucinous adenocarcinoma arising in chronic perianal fistula in a 34-year-old woman is being described. She presented with complaints of perineal fullness, pain and recurrent pus discharge from perianal fistula for 4 years. On radiological workup, a large solid-cystic pelvic mass was seen in relation to the fistula. On MRI, the lesion was mimicking a large horseshoe abscess. Transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy and subsequent histopathological examination confirmed the presence of mucinous adenocarcinoma with tumour cells immunopositive for CK7 and CK20.
https://ift.tt/2JmZDLK
Klebsiella endophthalmitis as the herald of occult colorectal cancer
A 67-year-old Chinese man presented with acute loss of vision and pain in the left eye with hypopyon in the anterior chamber. The patient was afebrile with no systemic symptoms at presentation. Diagnosis of endogenous endophthalmitis was made with vitreous tap yielding Klebsiella pneumoniae. Pars plana vitrectomy was performed twice to clear the infection. Thorough investigations showed no septic foci. Whole body positron emission tomography CT revealed a rectal tumour and biopsy showed adenocarcinoma. He was treated with neoadjuvant chemoirradiation followed by surgery to resect the tumour. Vision in the left eye was hand movement at 12 months postoperatively. This case illustrates Klebsiella endogenous endophthalmitis might be a herald of occult colorectal cancer. Bacteria might gain access into bloodstream via mucosal defect in the tumour.
https://ift.tt/2q8f29T
Native valve endocarditis, fusarium and end-stage renal disease
We would like to report a case of invasive Fusariosis involving the native mitral valve and complicated by septic thromboembolism. The patient was a known case of end-stage renal disease on maintenance haemodialysis and did not have any of the known risk factors for invasive Fusariosis like neutropaenia, severe T cell immunodeficiency, postsolid organ transplant recipients, posthaematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients and patients who received cytotoxic and/or high-dose corticosteroid therapy.
https://ift.tt/2JmPvmk
Epidermoid cyst within an intrapancreatic accessory spleen
This is a case of an epidermoid cyst in an intrapancreatic accessory spleen at the tail of the pancreas. Concurrent epidermoid cyst within the accessory spleen is an exceedingly rare entity. The patient initially presented with abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. Imaging studies revealed a 3.6 cm cystic mass in the tail of the pancreas that was concerning for a mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN). The patient underwent a robotic distal pancreatectomy for a suspected diagnosis of MCN, which following histologically examination was found to be an epidermoid cyst of an intrapancreatic accessory spleen. Further imaging characteristics are needed to characterise and differentiate these lesions from those of malignant potential. Robotic distal pancreatectomy is a safe alternative with many benefits including decreased length of stay and decreased blood loss.
https://ift.tt/2GA5orF
Infectious causes of Addisons disease: 1 organ--2 organisms!
Background
Infectious aetiologies are the most common causes of primary adrenal failure (Addison's disease) in low/middle-income countries while in the western world autoimmune causes predominate. The infections attributed to cause Addison's include disseminated gonococcal infection, tuberculosis, histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis and cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Here, we describe two classical cases of Addison's due to infections of the adrenal gland.
Case presentationCase 1A 55-year-old woman from North India was admitted with history of multiple episodes of vomiting. She had history of severe loss of appetite and loss of weight. There was also history of increased body pigmentation for the last 6 months. At admission, she was drowsy with tachycardia of 116 beats per minute and her blood pressure was 80/50 mm Hg in supine position associated with a significant postural drop. There was hyperpigmentation of fingers, face, oral mucosa and flexures. The rest of the system examination did not reveal any significant...
https://ift.tt/2qa5LOD
Uncommon presentation, rare complication and previously undescribed oncologic association of pheochromocytoma; the great masquerader
We describe the case of a 67-year-old man presenting with ventricular tachycardia (VT) and systolic heart failure secondary to a left adrenal phaeochromocytoma. After treatment with amiodarone, the patient's VT resolved. However, his course was complicated by femoral deep venous thrombosis secondary to an incidentally discovered dedifferentiated liposarcoma of the thigh, for which he was prescribed a course of enoxaparin. The patient was discharged with plans for adrenalectomy following achievement of sufficient preoperative heart rate and blood pressure control with alpha-adrenergic receptor blockade, but re-presented to an outside facility in haemorrhagic shock, where he ultimately expired. Autopsy determined his death to be caused by spontaneous haemorrhage of the phaeochromocytoma. Cardiac manifestations, complications and oncological associations of phaeochromocytoma are discussed.
https://ift.tt/2JnPlLC
Varicella-zoster virus necrotising retinitis, retinal vasculitis and panuveitis following uncomplicated chickenpox in an immunocompetent child
A 4-year-old girl presented with acute left visual loss 4 weeks after uneventful chickenpox. She was found to have left necrotising retinitis and profound retinal vasculitis and vitritis. Aqueous humour was PCR positive for varicella-zoster virus. Combined intravenous and intravitreal antiviral treatment led to rapid improvement with settled retinitis, no vascular occlusion and good recovery of vision. Her recent coinfection with Epstein-Barr virus may have acted to provoke the retinitis.
https://ift.tt/2EmnhUU
Isolated cystic lymphangiomatosis of spleen in an adult: a diagnostic conundrum
Lymphangiomatosis is a rare developmental disorder characterised by diffuse proliferation of anastomosing lymphatic channels (lymphangiomas). It is believed to result from anomalous lymphatic development and usually presents in childhood. It typically occurs as a part of systemic lymphangiomatosis and isolated organ involvement is rare. Only nine cases of isolated cystic lymphangiomatosis of spleen have been reported between 1990 and 2010. Tuberculosis is a significant health problem in India and varied forms of this disease are seen in clinical practice. Isolated splenic tuberculosis, though a rare entity, has been described in the Indian population. We present a case of isolated splenic lymphangiomatosis in a 42-year-old woman that was initially misdiagnosed as splenic tuberculosis and was treated accordingly. Unresponsive to medical treatment, the patient underwent splenectomy and on histopathological examination, cystic lymphangiomatosis was diagnosed. The patient's symptoms resolved after surgery and she is doing well at a follow-up of 3 months.
https://ift.tt/2Jld9PX
Hypocalcaemia in an adult: the importance of not overlooking the cause
A 58-year-old male patient was admitted at the São Bernardos's Hospital (Setúbal, Portugal) with generalised muscle spasms, dyspnoea, laryngospasm and bronchospasm in the context of severe hypocalcaemia. Despite efforts to correct serum calcium, it remained below average, leading to question the true cause of hypocalcaemia. Low parathyroid hormone and 25-hydroxyvitamin D, along with facial anomalies, palate defect and cognitive impairment with concomitant psychiatric disorder led to a suspicion of a DiGeorge/velocardiofacial/22q11.2 deletion syndrome (DS), which was confirmed through genetic testing. The 22q11.2 DS has a wide phenotypic expression and there are growing reports of diagnosis being made in adulthood. This case report highlights the importance of understanding the cause of refractory hypocalcaemia and alerts medical community to carefully access these patients, for this metabolic disorder may only present in later stages of life.
https://ift.tt/2qahCfF
Chiari malformation and tuberculous meningitis: aetiology and management
This is the first reported case of a Chiari 1 malformation in association with tuberculous (TB) meningitis. We present a case of a 23-year-old woman with a 2-week history nocturnal fever, vertigo, headache and projectile vomiting. She had nystagmus, scanning speech, bilateral papilloedema and ataxia. Cranial imaging showed a 10 mm tonsillar herniation. Posterior fossa decompression was done. Because the patient's gamut of symptoms was highly suspicious for a central nervous system infection, a lumbar tap was done which revealed TB meningitis. Four years later, after anti-TB medications and rehabilitation, all her symptoms except gait instability resolved.
https://ift.tt/2Gz3ism
Bilateral multifocal acute lobar nephronia caused by Enterococcus faecalis
An 8-year-old boy presented to our hospital with complaints of fever, epigastric pain and headache. Enterococcus faecalis were isolated from urine and blood culture, bacteraemic urinary tract infection was clinically diagnosed. Although vancomycin and ampicillin were administrated, fever did not subside. Contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) revealed bilateral and multiple wedge-shaped defects, thus prompting a diagnosis of acute lobar nephronia (ALN). After 7 days of antibiotic treatment, the patient's fever subsided. ALN can be classified into two subgroups based on features of CECT; simple and complicated ALN. The treatment response to antibiotics tends to be delayed in complicated ALN, it is important that we understand the natural course of complicated ALN and should not escalate antibiotics hastily. According to previous studies, ALN has a wide regional variety of causative organisms. Therefore, the physician should recognise a local pattern of microbiological aetiology of ALN.
https://ift.tt/2EmM1fM
Scorpion bite-induced unilateral pulmonary oedema
A 24-year-old woman came to the emergency room of our hospital, 6 hours after a sting to the pulp of her middle finger of her left upper limb by an Indian red scorpion. On examination, she had tachycardia, tachypnoea, hypotension and low oxygen saturation at room temperature. On auscultation, there was poor air entry in all areas of the right lung along with crackles. The left lung field was normal on auscultation. Chest X-ray showed unilateral haziness of right lung field. Two-dimensional echocardiography showed clinical findings of myocarditis. Arterial blood gas showed metabolic acidosis with severe hypoxaemia, suggestive of type 1 respiratory failure. After intubation and initiating ventillatory support, the patient was given intravenous analgesics, antihistaminic and infiltrated of site of bite with 2% xylocaine. The patient was started on inotropes, alpha receptor blocker, intravenous steroids, bronchodilators and diuretics support. The patient clinically improved over the course of treatment and was subsequently discharged.
https://ift.tt/2GzC30B
Rapunzel syndrome: a tail too long to tell!
Description
Trichobezoar leading to Rapunzel syndrome (RS) is an extremely rare entity with about 90 cases reported in literature.1 RS derives its name from the fairy tale 'Rapunzel', where the German princess let her long golden hair down from her tower to facilitate a tryst with her lover akin to the long and shiny tail of hair seen in RS.2 Hair being slippery gets trapped in gastric mucosal folds, eluding peristalsis. More and more hair conglomerate to form a stomach-shaped mass coated with mucus called trichobezoar. This provides it a shiny glistening surface, and the acid secreted in stomach denatures the hair protein which gives it the typical black colour.3 When the tail of hair extends beyond the stomach into the small intestine, it is called RS.
A 6-year-old girl presented to our emergency department with history of abdominal pain and recurrent vomiting for...
https://ift.tt/2Ely3uV
Immune stromal keratitis: a rare ocular presentation of tuberculosis
An 11-year-old female patient presented with diminution of vision in both the eyes for the last 4 days. She had redness, watering and photophobia for the past 11 days. Slit lamp examination revealed multiple disc-shaped corneal stromal infiltrates with an overlying epithelial defect and hypopyon in both the eyes. A provisional diagnosis of infective keratitis was made. The patient was started on empirical antimicrobial therapy. However, no improvement was noted over the next 72 hours. Microbiological examination of the corneal scraping from both the eyes was negative. Considering the above, provisional diagnosis was changed to immune stromal keratouveitis and the patient was started on topical steroids. Further evaluation revealed a positive Mantoux test (30x20 mm) and contrast enhanced CT chest showing pulmonary nodules, suggestive of tuberculosis. The patient was subsequently started on antitubercular treatment. The infiltrates along with the ulcer and anterior uveitis responded dramatically to the revised treatment and resolved completely within 7 days of therapy.
https://ift.tt/2GzBXpL
Perforated gastric remnant ulcer after laparoscopic gastric bypass
Ulcer perforation in the excluded stomach and duodenum is a rare complication after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). Pathogenesis of these ulcers are multifactorial. We report a case of perforated gastric remnant ulcer in a 54-year-old woman who had undergone a laparoscopic RYGB 5 years previously. The perforation was successfully repaired with an omental patch. We also present a review of the literature of similar cases.
https://ift.tt/2ElGbLy
Health professionals' and coroners' views on less invasive perinatal and paediatric autopsy: a qualitative study
Lewis, C; Hill, M; Arthurs, OJ; Hutchinson, JC; Chitty, LS; Sebire, N; (2018) Health professionals' and coroners' views on less invasive perinatal and paediatric autopsy: a qualitative study. Archives of Disease in Childhood 10.1136/archdischild-2017-314424 . (In press). Green open access
https://ift.tt/2GAv082
Alveolar T-helper 17 responses to streptococcus pneumoniae are preserved in ART-untreated and treated HIV-infected Malawian adults
Peno, C; Banda, DH; Jambo, N; Kankwatira, AM; Malamba, RD; Allain, TJ; Ferreira, DM; ... Jambo, KC; + view all Peno, C; Banda, DH; Jambo, N; Kankwatira, AM; Malamba, RD; Allain, TJ; Ferreira, DM; Heyderman, RS; Russell, DG; Mwandumba, HC; Jambo, KC; - view fewer (2018) Alveolar T-helper 17 responses to streptococcus pneumoniae are preserved in ART-untreated and treated HIV-infected Malawian adults. Journal of Infection , 76 (2) pp. 168-176. 10.1016/j.jinf.2017.10.013 . Green open access
https://ift.tt/2Emm93F
Beyond Jam Sandwiches and Cups of Tea: An Exploration of Primary Pupils’ Algorithm-Evaluation Strategies
Benton, L; Kalas, I; Saunders, P; Hoyles, C; Noss, R; (2018) Beyond Jam Sandwiches and Cups of Tea: An Exploration of Primary Pupils' Algorithm-Evaluation Strategies. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning (In press).
https://ift.tt/2JmRbMw
Identification of neural structures involved in stuttering using vibrotactile feedback
Cheadle, O; Sorger, C; Howell, P; (2018) Identification of neural structures involved in stuttering using vibrotactile feedback. Brain and Language (In press).
https://ift.tt/2q8Upuu
Immunosuppressive agents in adult kidney transplantation in the National Health Service: a model-based economic evaluation
Snowsill, TM; Moore, J; Mujica Mota, RE; Peters, JL; Jones-Hughes, TL; Huxley, NJ; Coelho, HF; ... Anderson, R; + view all Snowsill, TM; Moore, J; Mujica Mota, RE; Peters, JL; Jones-Hughes, TL; Huxley, NJ; Coelho, HF; Haasova, M; Cooper, C; Lowe, JA; Varley-Campbell, JL; Crathorne, L; Allwood, MJ; Anderson, R; - view fewer (2017) Immunosuppressive agents in adult kidney transplantation in the National Health Service: a model-based economic evaluation. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation , 32 (7) pp. 1251-1259. 10.1093/ndt/gfx074 .
https://ift.tt/2Gzi9mt
Risk factors for salivary gland cancers in France: Results from a case-control study, the ICARE study
![]()
Source:Oral Oncology, Volume 80
Author(s): Loredana Radoï, Christine Barul, Gwenn Menvielle, Matthieu Carton, Mireille Matrat, Marie Sanchez, Corinne Pilorget, Michel Velten, Isabelle Stücker, Danièle Luce
ObjectivesEpidemiological studies on the risk factors for salivary gland cancers (SGC) are rare, concern a small sample size, and show inconsistent results. The aim of the present work was to analyze several risk factors for SGC, using the data from the ICARE study, a multicenter, population-based case-control study.Materials and methodsData from 73 SGC cases and 3555 controls were collected using a standardized questionnaire on lifestyle habits, personal and family medical history, and lifetime occupational history. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were estimated using unconditional logistic regressions.ResultsTobacco use and alcohol consumption were not associated with the risk of SGC. A history of head and neck cancer or that of cervicofacial radiotherapy was associated with a higher risk of SGC (OR = 17.06, 95% CI: 4.34–67.05, and OR = 31.74, 2.48–405.25, respectively). Significantly increased risks were observed for some occupations: waiter (OR = 2.94, 1.11–7.78), charworker (OR = 3.02, 1.38–6.60), electrical and electronic equipment assembler (OR = 7.16, 2.02–25.38), plumber (OR = 3.95, 1.33–11.67), electric arc welder (OR = 6.15, 1.76–21.48), sheet-metal worker (OR = 2.89, 1.01–8.32), building painter (OR = 3.42, 1.01–11.49), and material handling equipment operator (OR = 5.05, 1.71–14.84). Results for industries were consistent with those observed for occupations.ConclusionOur results showed that a history of head and neck cancer, cervicofacial radiotherapy, and several occupations and industries, were associated with an increased risk of SGC. Further studies with larger sample sizes are indicated to confirm our results.
https://ift.tt/2GzMrFR
Hypoxia modulates CCR7 expression in head and neck cancers

Source:Oral Oncology, Volume 80
Author(s): Haneen A. Basheer, Edvinas Pakanavicius, Patricia A. Cooper, Steven D. Shnyder, Lisette Martin, Keith D. Hunter, Victoria Vinader, Kamyar Afarinkia
BackgroundThe chemokine receptor CCR7 is expressed on lymphocytes and dendritic cells and is responsible for trafficking of these cells in and out of secondary lymphoid organs. It has recently been shown that CCR7 expression is elevated in a number of cancers, including head and neck cancers, and that its expression correlates to lymph node (LN) metastasis. However, little is known about the factors that can induce CCR7 expression in head and neck cancers.MethodWe compared the protein expression and functional responses of CCR7 under normoxia and hypoxia in head and neck cancer cell lines OSC-19, FaDu, SCC-4, A-253 and Detroit-562 cultured as monolayers, spheroids, and grown in vivo as xenografts in balb/c mice. In addition, we analysed the correlation between hypoxia marker HIF-1α and CCR7 expression in a tissue microarray comprising 80 clinical samples with various stages and grades of malignant tumour and normal tissue.ResultsUnder hypoxia, the expression of CCR7 is elevated in both in vitro and in vivo models. Furthermore, in malignant tissue, a correlation is observed between hypoxia marker HIF-1α and CCR7 across all clinical stages. This correlation is also strong in early histological grade of tumours.ConclusionHypoxia plays a role in the regulation of the expression of CCR7 and it may contribute to the development of a metastatic phenotype in head and neck cancers through this axis.
https://ift.tt/2Em4s4h
Multi-criteria optimization achieves superior normal tissue sparing in intensity-modulated radiation therapy for oropharyngeal cancer patients
Publication date: May 2018
Source:Oral Oncology, Volume 80
Author(s): Jianghong Xiao, Yan Li, Huashan Shi, Tangel Chang, Yong Luo, Xuetao Wang, Yang He, Nianyong Chen
ObjectivesTo evaluate the benefit of intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) with multi-criteria optimization (MCO) in patients with oropharyngeal cancer (OPC) and compare the dose difference between the MCO plans navigated by physicians and dosimetrists.Materials and methodsThe conventional IMRT plans (nonMCO) and MCO IMRT plans navigated by physicians and dosimetrists (MCOp and MCOd) were created for 30patients with OPC. All the plans were reviewed, and the planning time and dose-volume parameters were compared.ResultsThe difference of D95 among three kinds of plans was not significant (p > 0.05). The maximum dose and D2 of spinal cord, brain stem, the mean dose of bilateral parotids, cochlea, oral cavity and glottic larynx were lower in MCO plans than those in nonMCO plans (p < 0.017). Furthermore, MCOp showed better bilateral parotids, oral cavity and glottic larynx sparing compared to MCOd (p < 0.017), in which the magnitude was related to the overlapping volume of the corresponding organ at risk (OAR) and targets. The active planning time was reduced by a median of 94.3 min (MCOd vs. nonMCO) or 91.6 min (MCOp vs. nonMCO).ConclusionMCO IMRT plans significantly reduced the dose of OARs and the active planning time, without compromising the target coverage in OPC patients; navigations by physicians could be beneficial to the dose sparing of the OARs with high complication rate and those overlapping with targets; the constraints could be the predominant factor affecting the results of optimization in the MCO IMRT planning.
Graphical abstract
https://ift.tt/2JlbkTj
A predictive model for recurrence in patients with glottic cancer implemented in a mobile application for Android

Source:Oral Oncology, Volume 80
Author(s): Ana Gabriela Jover-Esplá, Antonio Palazón-Bru, David Manuel Folgado-de la Rosa, Guillermo Severá-Ferrándiz, Manuela Sancho-Mestre, Joaquín de Juan-Herrero, Vicente Francisco Gil-Guillén
ObjectivesThe existing predictive models of laryngeal cancer recurrence present limitations for clinical practice. Therefore, we constructed, internally validated and implemented in a mobile application (Android) a new model based on a points system taking into account the internationally recommended statistical methodology.Materials and methodsThis longitudinal prospective study included 189 patients with glottic cancer in 2004–2016 in a Spanish region. The main variable was time-to-recurrence, and its potential predictors were: age, gender, TNM classification, stage, smoking, alcohol consumption, and histology. A points system was developed to predict five-year risk of recurrence based on a Cox model. This was validated internally by bootstrapping, determining discrimination (C-statistics) and calibration (smooth curves).ResultsA total of 77 patients presented recurrence (40.7%) in a mean follow-up period of 3.4 ± 3.0 years. The factors in the model were: age, lymph node stage, alcohol consumption and stage. Discrimination and calibration were satisfactory.ConclusionA points system was developed to obtain the probability of recurrence of laryngeal glottic cancer in five years, using five clinical variables. Our system should be validated externally in other geographical areas.
https://ift.tt/2Em4rxf
The clinical outcome and microbiological profile of bone-anchored hearing systems (BAHS) with different abutment topographies: a prospective pilot study
Abstract
Purpose
In this prospective clinical pilot study, abutments with different topologies (machined versus polished) were compared with respect to the clinical outcome and the microbiological profile. Furthermore, three different sampling methods (retrieval of abutment, collection of peri-abutment exudate using paper-points, and a small peri-abutment soft-tissue biopsy) were evaluated for the identification and quantification of colonising bacteria.
Methods
Twelve patients, seven with machined abutment and five with polished abutment, were included in the analysis. Three different sampling procedures were employed for the identification and quantification of colonising bacteria from baseline up to 12 months, using quantitative culturing. Clinical outcome measures (Holgers score, hygiene, pain, numbness and implant stability) were investigated.
Results
The clinical parameters, and total viable bacteria per abutment or in tissue biopsies did not differ significantly between the polished and machined abutments. The total CFU/mm2 abutment and CFU/peri-abutment fluid space of anaerobes, aerobes and staphylococci were significantly higher for the polished abutment. Anaerobic bacteria were detected in the tissue biopsies before BAHS implantation. Anaerobes and Staphylococcus spp. were detected in all three compartments after BAHS installation. For most patients (10/12), the same staphylococcal species were found in at least two of the three compartments at the same time-point. The common skin coloniser Staphylococcus epidermidis was identified in all patients but one (11/12), whereas the pathogen Staphylococcus aureus was isolated in five of the patients. Several associations between clinical and microbiological parameters were found.
Conclusions
There was no difference in the clinical outcome with the use of polished versus machined abutment at 3 and 12 months after implantation. The present pilot trial largely confirmed a suitable study design, sampling and analytical methodology to determine the effects of modified BAHS abutment properties.
Level of evidence
2. Controlled prospective comparative study.
https://ift.tt/2GCpW2P
Stream of Consciousness
In this Journal feature, information about a real patient is presented in stages (boldface type) to an expert clinician, who responds to the information, sharing his or her reasoning with the reader (regular type). The authors' commentary follows. A 65-year-old man presented to an emergency room in…
https://ift.tt/2q6wtIP
Vaccination against IL-31 for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in dogs
![]()
Source:Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Author(s): Martin F. Bachmann, Andris Zeltins, Gints Kalnins, Ina Balke, Nina Fischer, Ana Rostaher, Kaspars Tars, Claude Favrot
https://ift.tt/2GA4V4U
Th1/Th17 cell recognition of desmoglein 3 and bullous pemphigoid antigen 180 in lichen planus
![]()
Source:Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Author(s): Thomas Schmidt, Farzan Solimani, Robert Pollmann, Ronja Stein, Ansgar Schmidt, Inna Stulberg, Katja Kühn, Rüdiger Eming, Verena Eubel, Peter Kind, Nicole Arweiler, Cassian Sitaru, Michael Hertl
Teaser
We identified Th1/Th17 cell responses against desmoglein 3 and bullous pemphigoid antigen 180 in lichen planus. In contrast, patients with pemphigus vulgaris and bullous pemphigoid showed significantly higher Th2 cell responses against these autoantigens.https://ift.tt/2GTdZVZ
Correlation of allergen-specific T follicular helper cells with specific IgE and efficacy of allergen immunotherapy
![]()
Source:Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Author(s): Yin Yao, Cai-Ling Chen, Nan Wang, Zhi-Chao Wang, Jin Ma, Rong-Fei Zhu, Xiao-Yan Xu, Peng-Cheng Zhou, Di Yu, Zheng Liu
Teaser
Allergen-specific IL-4+ Tfh cells may contribute to allergen-specific IgE production and correlate with clinical efficacy of AIT in AR patients, which may be a promising therapeutic target and biomarker for AIT in AR.https://ift.tt/2IuWZCo
Obesity and asthma
Publication date: April 2018
Source:Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Volume 141, Issue 4
Author(s): Ubong Peters, Anne E. Dixon, Erick Forno
Information for Category 1 CME CreditCredit can now be obtained, free for a limited time, by reading the review articles in this issue. Please note the following instructions.Method of Physician Participation in Learning Process: The core material for these activities can be read in this issue of the Journal or online at the JACI Web site: www.jacionline.org. The accompanying tests may only be submitted online at www.jacionline.org. Fax or other copies will not be accepted.Date of Original Release: April 2018. Credit may be obtained for these courses until March 31, 2019.Copyright Statement: Copyright © 2018-2019. All rights reserved.Overall Purpose/Goal: To provide excellent reviews on key aspects of allergic disease to those who research, treat, or manage allergic disease.Target Audience: Physicians and researchers within the field of allergic disease.Accreditation/Provider Statements and Credit Designation: The American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI) is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide continuing medical education for physicians. The AAAAI designates this journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1.00 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit™. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.List of Design Committee Members: Ubong Peters, PhD, Anne E. Dixon, MA, BM, BCh, and Erick Forno, MD, MPH (authors); Andrea Apter, MD, MA, MSc (editor)Disclosure of Significant Relationships with Relevant CommercialCompanies/Organizations: A. E. Dixon has received grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Lung Association, and Pfizer and has received personal fees from Vitaeris. The rest of the authors declare that they have no relevant conflicts of interest. A. Apter (editor) declares that she has no relevant conflicts of interest.Activity Objectives:1. To understand the role that obesity plays as a risk factor for and disease modifier of asthma.2. To identify the mechanisms involved in asthma pathogenesis.3. To understand the evidence supporting lifestyle changes in influencing disease progression.4. To identify the clinical characteristics of obese asthma in children and adults.Recognition of Commercial Support: This CME activity has not received external commercial support.List of CME Exam Authors: Gagandeep Cheema, MD, Erica Ridley, MD, Eliane Abou-Jaoude, MD, and Christian Nageotte, MD.Disclosure of Significant Relationships with Relevant CommercialCompanies/Organizations: The exam authors disclosed no relevant financial relationships.Obesity is a vast public health problem and both a major risk factor and disease modifier for asthma in children and adults. Obese subjects have increased asthma risk, and obese asthmatic patients have more symptoms, more frequent and severe exacerbations, reduced response to several asthma medications, and decreased quality of life. Obese asthma is a complex syndrome, including different phenotypes of disease that are just beginning to be understood. We examine the epidemiology and characteristics of this syndrome in children and adults, as well as the changes in lung function seen in each age group. We then discuss the better recognized factors and mechanisms involved in disease pathogenesis, focusing particularly on diet and nutrients, the microbiome, inflammatory and metabolic dysregulation, and the genetics/genomics of obese asthma. Finally, we describe current evidence on the effect of weight loss and mention some important future directions for research in the field.
https://ift.tt/2GX4qVL
Treating insect-bite hypersensitivity in horses with active vaccination against IL-5
Publication date: Available online 4 April 2018
Source:Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Author(s): Antonia Fettelschoss-Gabriel, Victoria Fettelschoss, Franziska Thoms, Christoph Giese, Michelle Daniel, Florian Olomski, Jivko Kamarachev, Katharina Birkmann, Maya Bühler, Martin Kummer, Andris Zeltins, Eliane Marti, Thomas M. Kündig, Martin F. Bachmann
BackgroundInsect-bite hypersensitivity is the most common allergic dermatitis in horses. Excoriated skin lesions are typical symptoms of this seasonal and refractory chronic disease. On a cellular level, the skin lesions are characterized by massive eosinophil infiltration caused by an underlying allergic response.ObjectiveTo target these cells and treat disease, we developed a therapeutic vaccine against equine IL-5 (eIL-5), the master regulator of eosinophils.MethodsThe vaccine consisted of eIL-5 covalently linked to a virus-like particle derived from cucumber mosaic virus containing the tetanus toxoid universal T-cell epitope tt830-843 (CMVTT). Thirty-four Icelandic horses were recruited and immunized with 400 μg of eIL-5–CMVTT formulated in PBS without adjuvant (19 horses) or PBS alone (15 horses).ResultsThe vaccine was well tolerated and did not reveal any safety concerns but was able to induce anti–eIL-5 autoantibody titers in 17 of 19 horses. This resulted in a statistically significant reduction in clinical lesion scores when compared with previous season levels, as well as levels in placebo-treated horses. Protection required a minimal threshold of anti–eIL-5 antibodies. Clinical improvement by disease scoring showed that 47% and 21% of vaccinated horses reached 50% and 75% improvement, respectively. In the placebo group no horse reached 75% improvement, and only 13% reached 50% improvement.ConclusionOur therapeutic vaccine inducing autoantibodies against self IL-5 brings biologics to horses, is the first successful immunotherapeutic approach targeting a chronic disease in horses, and might facilitate development of a similar vaccine against IL-5 in human subjects.
Graphical abstract
https://ift.tt/2IudVc9
Obesity and asthma
Publication date: April 2018
Source:Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Volume 141, Issue 4
https://ift.tt/2GTdYBp
The Editors' Choice
![]()
Source:Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Volume 141, Issue 4
Author(s): Zuhair K. Ballas
https://ift.tt/2IvQqQh
News Beyond Our Pages
![]()
Source:Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Volume 141, Issue 4
Author(s): Marc E. Rothenberg, Jean Bousquet
https://ift.tt/2GWhYRm
Role of the Microbiome in Food Allergy
Abstract
Purpose of Review
Resident microbial communities likely modify risk for allergic disorders, including food allergy. We review epidemiologic studies linking microbial exposures to food allergy risk and discuss the mechanisms by which the microbiome may modulate oral tolerance. We additionally address ongoing translational efforts in human microbiome studies.
Recent Findings
Epidemiologic studies and murine models support that altered microbial exposures and colonization in early life modify food allergy risk. Differential microbiota confer protection or susceptibility to food allergy by modulating the regulatory tone of the mucosal immune system. Recent efforts are focused on the identification of bacterial strains necessary for oral tolerance in human and microbial-based clinical trials.
Summary
Early childhood appears to be critical for the colonization of a diverse microbiota necessary for the induction and maintenance of oral tolerance. Identification and functional evaluation of protective commensal microbes will inform strategies for the prevention and treatment of food allergy.
https://ift.tt/2JkC0Dv
