Publication date: Available online 2 July 2018
Source:Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
Author(s): Erica Jackson Mayland, Anna M. Pou
Salivary gland tumors are an uncommon heterogeneous group of neoplasms that vary in their anatomic site, histology and biologic behavior. Pleomorphic adenoma is the most common benign tumor and mucoepidermoid and adenoid cystic carcinoma are the most common malignant tumors. Evaluation and diagnosis of these tumors includes not only a complete history and head and neck exam, but also biopsy and imaging of the tumors. Controversy remains regarding the necessity and type of biopsy to be performed and the usefulness of imaging. This manuscript describes the utility of different diagnostic procedures in evaluating salivary gland neoplasms.
https://ift.tt/2IMrljJ
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2020
(289)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
►
2019
(9071)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (3642)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (3200)
-
▼
2018
(39872)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3318)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (3683)
-
▼
Ιουλίου
(3378)
-
▼
Ιουλ 02
(53)
- Evaluation and Diagnosis of Salivary Gland Neoplasms
- Spread of blaCTX-M-15-producing Enterobacteriaceae...
- Is it time for systematic voriconazole pharmacogen...
- Broad-spectrum adaptive antibiotic resistance asso...
- Rapid antibiotic combination testing for carbapene...
- Characterization of a novel SXT/R391 Integrative a...
- Azithromycin in combination with ceftriaxone reduc...
- Pharmacodynamic target attainment for cefepime, me...
- Gold nanoparticle conjugated Cinnamic acid exhibit...
- Prevalence and genetic analysis of mcr-3-positive ...
- Superior Pyronaridine Single Dose Pharmacodynamics...
- Prevalence of Inappropriate Antibiotic Prescribing...
- Predictors of Peripherally Inserted Central Cathet...
- Clinical regimens of favipiravir inhibit Zika viru...
- Four Japanese Patients with Congenital Nephrogenic...
- Recurrent FPIES to wheat after multiple tolerant e...
- Unusual case of primary spontaneous hemopneumothor...
- Intraoperative thermal safety of endoscopic ear su...
- Chronic Deafness Degrades Temporal Acuity in the E...
- A population-based epidemiological study of anaphy...
- Reflection- and Distortion-Source Otoacoustic Emis...
- Health-Related Quality of Life of Community Thyroi...
- Mid- to Late-Life Increases in Marker of Chronic I...
- Objective measures of physical activity in patient...
- Experimental Drug Stops Parkinson’s Disease Progre...
- Banana fruit: An “appealing” alternative for pract...
- Ixekizumab provides superior efficacy compared to ...
- The Use of a Tympanoplasty Blade for Tumor Extirpa...
- Natural History of Disease Activity and Damage in ...
- Choosing the Right Biologic for Psoriatic Patients...
- Peripheral monocytes and neutrophils predict respo...
- Successful desensitization in a pediatric patient ...
- Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy: div...
- Health Literacy and Asthma Among Hispanic and Afri...
- Specific-IgE to galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (alp...
- Efficacy of C1Inhibitor concentrate in hereditary ...
- Combo-VAS: an integrated outcome for assessing the...
- Mary Hewitt Loveless, MD, and the origin of venom ...
- Chronic Tearing Induced by Apremilast
- The T-win® technology: immune-modulating vaccines
- Acquired resistance to cancer immunotherapy
- Gabapentin, Methadone, and Oxycodone With or Witho...
- Wearable Sensor for Biometrics During Locoregional...
- Sitravatinib (MGCD516) and Nivolumab in Oral Cavit...
- Nivolumab & IRX-2 With Surgery for Resectable Stag...
- TPF Induction Chemotherapy vs PF Adjuvant Chemothe...
- Computer Algorithm Maps Cancer Resistance to Drugs...
- mTOR-mediated glycolysis contributes to the enhanc...
- Making a Difference by Addressing Social Determina...
- Sinus computed tomography predicts clinical respon...
- Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia (epith...
- Complete small bowel obstruction without intussusc...
- Gallstone ileus 1 year after cholecystectomy
-
▼
Ιουλ 02
(53)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (2693)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (3198)
-
►
2017
(41099)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (3127)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (2173)
-
►
2016
(13807)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (700)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (600)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (1350)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (1400)
-
►
2015
(1500)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (1450)
Ετικέτες
Δευτέρα 2 Ιουλίου 2018
Evaluation and Diagnosis of Salivary Gland Neoplasms
Spread of blaCTX-M-15-producing Enterobacteriaceae and OXA-23-producing Acinetobacter baumannii ST2 in Tunisian seafood [PublishAheadOfPrint]
Bivalves are filter-feeding animals and markers of bacterial pollution. We report a massive spread of blaCTX-M-15 through dominant E. coli and K. pneumoniae lineages and/or plasmid subtypes (F31:A4:B1) as well as OXA-23-producing Acinetobacter baumannii ST2 in seafood, highlighting a direct risk for the consumer. These findings should urge authorities to consider hospital effluents, but also farm and urban effluents, as important sources of ESBL/carbapenemase-producers that filter-feeding animals can concentrate and further spread to humans.
https://ift.tt/2KHgPMk
Is it time for systematic voriconazole pharmacogenomic investigation for central nervous system aspergillosis? [PublishAheadOfPrint]
Voriconazole is the standard treatment for invasive aspergillosis but requires therapeutic drug monitoring for optimizing therapy. We report two cases of central nervous system aspergillosis treated with voriconazole. Because of low trough plasma concentrations, we identified gain-of-function mutations of CYP2C19 that were partially responsible for therapeutic failure of voriconazole. We suggest systematic voriconazole pharmacogenomic investigation in cerebral aspergillosis to avoid effective therapy delay in this life-threatening disease.
https://ift.tt/2KsiZU9
Broad-spectrum adaptive antibiotic resistance associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucin-dependent surfing motility [PublishAheadOfPrint]
Surfing motility is a novel form of surface adaptation exhibited by the nosocomial pathogen, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, in the presence of the glycoprotein mucin that is found in high abundance at mucosal surfaces especially the lungs of cystic fibrosis and bronchiectasis patients. Here we investigated the adaptive antibiotic resistance of P. aeruginosa under conditions in which surfing occurs compared to cells undergoing swimming. P. aeruginosa surfing cells were significantly more resistant to several classes of antibiotics including aminoglycosides, carbapenems, polymyxins, and fluroquinolones. This was confirmed by incorporation of antibiotics into growth medium, which revealed a concentration-dependent inhibition of surfing motility that occurred at concentrations much higher than those needed to inhibit swimming. To investigate the basis of resistance, RNA-Seq was performed and revealed that surfing influenced the expression of numerous genes. Included amongst genes dysregulated under surfing conditions were multiple genes from the Pseudomonas resistome, which are known to affect antibiotic resistance when mutated. Screening transposon mutants in these surfing-dysregulated resistome genes revealed that several of these mutants exhibited changes in susceptibility to one or more antibiotics under surfing conditions, consistent with a contribution to the observed adaptive resistance. In particular, several mutants in resistome genes, including armR, recG, atpB, clpS, nuoB, and certain hypothetical genes such as PA5130, PA3576 and PA4292, showed contributions to broad-spectrum resistance under surfing conditions and could be complemented by their respective cloned genes. Therefore, we propose that surfing adaption led to extensive multidrug adaptive resistance as a result of the collective dysregulation of diverse genes.
https://ift.tt/2IMUtHu
Rapid antibiotic combination testing for carbapenem-resistant Gram negative bacteria within 6h using adenosine triphosphate bioluminescence [PublishAheadOfPrint]
To guide the timely selection of antibiotic combinations against carbapenem-resistant Gram negative bacteria (CR-GNB), an in vitro test with a short turn-around time is essential. We developed an in vitro ATP bioluminescent assay to determine effective antibiotic combinations against CR-GNB within 6h. We tested 42 clinical CR-GNB strains (14 Acinetobacter baumannii, 14 Pseudomonas aeruginosa and 14 Klebsiella pneumoniae) against 74 single and two-antibiotic combinations. Approximately 5log10 CFU/ml bacteria were incubated with antibiotic(s) at 35°C, and ATP bioluminescence was measured at 6h and 24h, and compared to 24h viable counts. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to determine the optimal thresholds (TRLU) for differentiating between inhibitory and non-inhibitory combinations. The area under the 6h and 24h ROC curves were compared using the DeLong method. Prospective validation of the established thresholds was conducted using 18 additional CR-GNB. The predictive accuracy of TRLU for the 6h ATP bioluminescence assay was 77.5% for when all species were collectively analyzed. Predictive accuracies ranged from 73.7% – 82.7% when each species were individually analyzed. Upon comparison of the area under the 6h and 24h ROC curves, the 6h assay performed significantly better (p <0.01). Predictive accuracy remained high upon prospective validation of the 6h ATP assay (predictive accuracy, 79.8%; 95% CI, 77.6 – 81.9%), confirming the external validity of the assay. Our findings indicate that our 6h ATP bioluminescence assay can provide guidance for prospective combination selection against CR-GNB in a timely manner, and may be useful in the management of CR-GNB infections.
https://ift.tt/2KAL7nh
Characterization of a novel SXT/R391 Integrative and Conjugative Element carrying cfr, blaCTX-M-65, fosA3 and aac(6')-Ib-cr in Proteus mirabilis [PublishAheadOfPrint]
A novel 139,487-bp SXT/R391 Integrative and Conjugative Element, ICEPmiChnBCP11, was characterized in Proteus mirabilis of swine origin in China. ICEPmiChnBCP11 harbors twenty different antimicrobial resistance genes, including clinically important rRNA methyltransferase gene cfr, extended-spectrum β-lactamase gene blaCTX-M-65, fosfomycin resistance gene fosA3 and fluoroquinolones resistance gene aac(6')-Ib-cr. An ISPpu12-mediated composite transposon containing various resistance genes and ten copies of IS26 is inserted in hot spot 4. ICEPmiChnBCP11 was successfully transferred to Escherichia coli.
https://ift.tt/2KHbQvc
Azithromycin in combination with ceftriaxone reduces systemic inflammation and provides survival benefit in murine model of polymicrobial sepsis [PublishAheadOfPrint]
Sepsis is a life threatening systemic inflammatory condition triggered as a result of excessive host immune response to infection. In the past, immunomodulators have demonstrated protective effect in sepsis. Azithromycin (macrolide antibiotic) having immunomodulatory activity was therefore evaluated in combination with ceftriaxone in a clinically relevant murine model of sepsis induced by caecal ligation and puncture (CLP). First, mice underwent CLP and 3 h later were administered with vehicle or sub-protective dose of ceftriaxone (100 mg/kg, subcutaneous) alone or in combination with immunomodulatory dose of azithromycin (100 mg/kg, intraperitoneal). Survival was monitored for 5 days. In order to assess the immunomodulatory activity, parameters such as plasma and lung cytokines concentrations (interleukin IL-6, IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α), plasma glutathione (GSH), plasma and lung myeloperoxidase (MPO), body temperature, blood glucose, total white blood cell count, along with bacterial load in blood, peritoneal fluid and lung homogenate were measured 18 h after CLP challenge. Azithromycin in presence of ceftriaxone significantly improved the survival of CLP challenged mice. Further, the combination attenuated the elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines and MPO in plasma and lung tissue and increased the body temperature, blood glucose and GSH which were otherwise markedly decreased in CLP mice. Ceftriaxone exhibited significant reduction in bacterial load, while co-administration of azithromycin did not show further reduction. Therefore, the survival benefit by azithromycin was due to immunomodulation and not by its antibacterial action. Findings of this study indicate that azithromycin could provide clinical benefits in sepsis in conjunction with appropriate antibacterial agents.
https://ift.tt/2KrQXrQ
Pharmacodynamic target attainment for cefepime, meropenem and piperacillin/tazobactam using a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic-based dosing calculator in critically ill patients [PublishAheadOfPrint]
This was a prospective study to determine if pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD)-based antibiotic dosing software aids in achieving concentration targets in critically ill patients receiving cefepime (n=10), meropenem (n=20), or piperacillin/tazobactam (n=19). Antibiotic calculator doses targeting >90% probability of target attainment (PTA) differed from package-insert doses for 22.4% (11/49) patients. Target attainment was achieved for 98% of patients (48/49). A PK/PD based antibiotic dosing calculator provides beta-lactam doses with high likelihood of PTA in critically ill patients.
https://ift.tt/2KEUDSR
Gold nanoparticle conjugated Cinnamic acid exhibit Antiacanthamoebic and antibacterial properties [PublishAheadOfPrint]
Trans-Cinnamic acid (CA) is a natural organic compound. Using amoebicidal assays, for the first time we showed that CA affected viability of protist pathogen, Acanthamoeba castellanii. Conjugation with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) enhanced antiamoebic effects of CA. Cinnamic acid coated gold nanoparticles (CA-AuNPs) also exhibited significant excystation and encystation activity as compared to CA and AuNPs alone. Pre-treatment of amoebae with CA-AuNPs inhibited A. castellanii-mediated host cell cytotoxicity. Moreover, CA-AuNPs exhibited potent effects against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, and neuropathogenic Escherichia coli K1 as well as protected host cells against bacterial-mediated host cell death.
https://ift.tt/2KqYBTo
Prevalence and genetic analysis of mcr-3-positive Aeromonas species from humans, retail meat, and environmental water samples [PublishAheadOfPrint]
The mobile colistin-resistance gene mcr-3 is globally disseminated in both Enterobacteriaceae and Aeromonas species, the latter of which potentially serves as a reservoir for this gene. Here, we investigated the prevalence of mcr-3 from rectal swabs of humans, food-producing animals and their products, and the aquatic environment, and investigated the genetic relationships between the mcr-3-positive isolates. An enriched broth screening method was used to detect mcr-3 in samples, and species identification of isolates from the positive samples was carried out by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and shotgun sequencing. All mcr-3-positive isolates were subjected to antimicrobial susceptibility testing, conjugation, and whole genome sequencing. Ten Aeromonas isolates, two from human rectal swabs, one from pork, three from chicken meat, and four from the aquatic environment, were positive for mcr-3, but only two showed resistance to colistin. Besides the mcr-3-variants identified before– the novel variants were termed mcr-3.13 to mcr-3.18 – all isolates also harbored mcr-3-like genes downstream of the mcr-3 variants. The MCR-3.13 to MCR-3.18 proteins exhibited only 84–85% amino acid identity to the original MCR-3 protein. Whole genome sequence analysis indicated diversity within the genetic environment of mcr-3-positive Aeromonas isolates, and possible transmission between different sources in China, and even worldwide. Close relationships between mcr-3-positive and -negative Aeromonas isolates suggested that mcr-3 might be common in Aeromonas species, which are not inherent hosts of mcr-3 but may act as an important reservoir of this mobile colistin-resistance gene.
https://ift.tt/2KDV6ou
Superior Pyronaridine Single Dose Pharmacodynamics Compared to Artesunate, Chloroquine and Amodiaquine In A Murine Malaria-Luciferase Model [PublishAheadOfPrint]
Many previous in vitro and in vivo preclinical malaria drug studies have relied on low parasite number drug inhibition numerically compared to untreated controls. In contrast, human malaria drug studies measure the high parasite density killing near 100 million/mL. Here we compared the in vivo single dose pharmacodynamic properties of artesunate and 4-aminoquinolines-pyronaridine, chloroquine, and amodiaquine, in a Plasmodium bergheiANKA-GFP-Luciferase-based murine malaria blood stage model. Pyronaridine exhibited dose-dependent killing, achieving parasite reduction near 5-6 logs at 48 hours with complete cure at 10 mg/kg compared to artesunate, which exhibited a 48 hour dose-dependent killing with a 2 log drop at the noncurative 250 mg/kg dose. Chloroquine, noncurative, and amodiaquine, partially curative, have nearly the same initial dose-independent killing with a lag phase of minimal parasite reduction at all doses between 6 and 24 hours, followed by 2.5 log reduction at 48 hours. In drug treated, washed infected blood transfer experiments to naïve mice, chloroquine and amodiaquine showed less viable parasites at the 24 hour compared to 8 hour transfer measured by a prolonged return to parasitemia, despite a similar parasite log reduction at these time points, in contrast to the correlation of parasite log reduction to viable parasites with artesunate and pyronaridine. Artesunate in combination with pyronaridine exhibited a similar initial parasite reduction to pyronaridine, while with chloroquine or amodiaquine, the reduction was similar to artesunate. Single oral dose pyronaridine was much more potent in vivo than artesunate, chloroquine and amodiaquine during the initial decline in parasites and cure.
https://ift.tt/2KEVq9K
Prevalence of Inappropriate Antibiotic Prescribing in Primary Care Clinics within a Veterans Affairs Healthcare System [PublishAheadOfPrint]
Data are needed from outpatient settings to better inform antimicrobial stewardship. In this study, a random sample of outpatient antibiotic prescriptions by primary care providers (PCPs) at our healthcare system was reviewed and compared to consensus guidelines. Over twelve months, 3,880 acute antibiotic prescriptions were written by 76 PCPs caring for 40,734 patients (median panel 600 patients; range 33-1,547). PCPs ordered a median of 84 antibiotic prescriptions per 1,000 patients per year. Azithromycin (25.8%), amoxicillin-clavulanate (13.3%), doxycycline (12.4%), amoxicillin (11%), fluoroquinolones (11%), and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (10.6%) were prescribed most commonly. Medical records corresponding to 300 prescriptions from 59 PCPs were analyzed in depth. The most common indications for these prescriptions were acute respiratory tract infection (28.3%), urinary tract infection (23%), skin and soft tissue infection (15.7%), and COPD exacerbation (6.3%). In 5.7% of cases, no reason for the prescription was listed. No antibiotic was indicated in 49.7% of cases. In 12.3% of cases, an antibiotic was indicated but the prescribed agent was guideline-discordant. In another 14% of cases, a guideline-concordant antibiotic was given for a guideline-discordant duration. Therefore, 76% of reviewed prescriptions were inappropriate. Ciprofloxacin and azithromycin were most likely to be prescribed inappropriately. A non-face-to-face encounter prompted 34% of prescriptions. The condition for which an antibiotic was prescribed was not listed in primary or secondary diagnosis codes in 54.5% of clinic visits. In conclusion, there is an enormous opportunity to reduce inappropriate outpatient antibiotic prescriptions.
https://ift.tt/2IKieQl
Predictors of Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter Occlusion in the Outpatient Parenteral Antimicrobial Therapy Setting [PublishAheadOfPrint]
In this retrospective study of 285 patients receiving outpatient parenteral antibiotic therapy (OPAT), duration of antibiotic, use of double-lumen catheters, and receipt of penicillin G and cloxacillin appeared to increase the risk of PICC occlusion. Physicians should consider these factors when prescribing long-term antibiotic therapy. Further studies are needed to evaluate methods to reduce PICC occlusion, particularly when double-lumen PICCs are necessary, and when cloxacillin or penicillin G are the preferred treatment.
https://ift.tt/2KoxOa2
Clinical regimens of favipiravir inhibit Zika virus (ZIKV) replication in the Hollow Fiber Infection Model (HFIM) [PublishAheadOfPrint]
Zika virus (ZIKV) infection is associated with serious, long-term neurological manifestations. There are currently no approved therapies for the treatment or prevention of ZIKV. Favipiravir (FAV) is a viral polymerase inhibitor with broad-spectrum activity. Our prior studies used static FAV concentrations and demonstrated promising activity. However, the anti-ZIKV activity of dynamic FAV concentrations has never been evaluated in a human cell line. Here we employed the hollow fiber infection model (HFIM) to simulate human pharmacokinetic (PK) profiles associated with clinically-utilized influenza and Ebola FAV dosage regimens and assess the viral burden profiles. Clinically achievable FAV concentrations inhibited ZIKV replication in HUH-7 cells in a dose-dependent fashion (EC50 = 236.5 uM). The viral burden profiles under dynamic FAV concentrations were predicted by mechanism-based mathematical modeling (MBM) and subsequently successfully validated in the HFIM. This validated, translational MBM can now be used to predict the anti-ZIKV activity for other FAV dosage regimens in presence of between patient variability in pharmacokinetics. This approach can be extended to rationally optimize FAV combination dosage regimens which hold promise to treat ZIKV infections in non-pregnant patients.
https://ift.tt/2KDUJu6
Four Japanese Patients with Congenital Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus due to the AVPR2 Mutations
Almost 90% of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI) is caused by mutations in the arginine vasopressin receptor 2 gene (AVPR2) on the X chromosome. Herein, we reported clinical and biochemical parameters in four cases of three unrelated Japanese families and analyzed the status of the AVPR2. Two of the four patients had poor weight gain. However, in the male and female sibling cases, neither had poor weight gain while toddlers, but in the male sibling, episodes of recurrent fever, polyuria, and polydipsia led to the diagnosis of NDI at 4 years of age. Analysis of AVPR2 identified two nonsense mutations (c.299_300insA; p.K100KfsX91 and c.296G > A; p.W99X) and one missense mutation (c.316C > T; p.R106C). These mutations were previously reported. The patient with c.316C > T; p.R106C had milder symptoms consistent with previous reports. Of the familial cases, the sister was diagnosed as having NDI, but a skewed X-inactivation pattern in her peripheral blood lymphocytes was not identified. In conclusion, our study expands the spectrum of phenotypes and characterized mutations in AVPR2 in NDI.
https://ift.tt/2lR2UbP
Recurrent FPIES to wheat after multiple tolerant exposures in a male infant
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome (FPIES) is a non-IgE mediated reaction to food that typically presents in infancy and manifests as repetitive vomiting, lethargy and hypotension 1 to 4 hours after ingestion, occasionally followed by delayed diarrhea. Due to lack of a diagnostic biomarker, oral food challenge (OFC) remains the gold standard for diagnosis of FPIES and to monitor for resolution. Supervised introduction of high-risk foods has also been recommended given the high rate of cross-reactivity of some foods.
https://ift.tt/2KrfZHF
Unusual case of primary spontaneous hemopneumothorax in a young man with atypical tension pneumothorax: a case report
Spontaneous life-threatening hemopneumothorax is an atypical but treatable entity of unexpected circulatory collapse in young patients, affecting 0.5–11.6% of patients with primary spontaneous pneumothorax. Sp...
https://ift.tt/2lR6yCw
Intraoperative thermal safety of endoscopic ear surgery utilizing a holder
Despite the ever-growing popularity of endoscopic ear surgery (EES), there are still concerns regarding the potential thermal risk associated with the use of light sources and also questions raised about the thermal safety of extended stationary applications of endoscopes with holders that allow the use of both hands in the middle ear. The temperature changes witnessed during EES when using different calipers on static endoscopes fitted with camera holders during true operations were measured, and effects of varying light source intensities, as well as the cooling effect of irrigation and suction, were investigated.
https://ift.tt/2lOF0NV
Chronic Deafness Degrades Temporal Acuity in the Electrically Stimulated Auditory Pathway
Abstract
Electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve with a penetrating intraneural (IN) electrode in acutely deafened cats produces much more restricted spread of excitation than is obtained in that preparation with a conventional cochlear implant (CI) as reported by Middlebrooks and Snyder (J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 8:258–279, 2007). That suggests that a future auditory prosthesis employing IN stimulation might offer human patients greater frequency selectivity than is available with a present-day CI. Nevertheless, it is a concern that the electrical field produced by an IN electrode might be too restricted to produce adequate stimulation of the partially depopulated auditory nerve of a deaf patient. We evaluated this by testing responses to IN and CI stimulation in adult-deafened cats. Activation of the auditory pathway was monitored by recording from the central nucleus of the inferior colliculus (ICC). Cats deaf for 153–277 days exhibited a ~ 30 % loss of auditory nerve fibers compared to cats deaf for < 18 h. Contrary to our concern, measures of thresholds and dynamic ranges showed no significant deafness-related impairment of excitation by IN or CN stimulation. Surprisingly, however, temporal acuity decreased dramatically in these adult-deafened cats, as demonstrated by a marked decrease in the maximum rate of electrical cochlear stimulation to which ICC neurons synchronized to IN or CI stimulation. For instance, half of ICC neurons synchronized to IN stimulation up to 203 pulses per second (pps) in acute deafness, whereas that number dropped to 79 pps for chronic deafness. Such a loss of temporal acuity might contribute to the poor sensitivity to temporal fine structure that has been reported in human CI users. Seemingly, the degraded temporal acuity that we observed in cats was even worse than the fine-structure sensitivity of human CI users, suggesting that most patients experience some improvement of temporal acuity resulting from restoration of patterned auditory nerve stimulation by a CI.
https://ift.tt/2lNpMsH
A population-based epidemiological study of anaphylaxis using national big data in Korea: trends in age-specific prevalence and epinephrine use in 2010–2014
Previous reports on anaphylaxis in Asia are limited to relatively small-scale studies. We performed this study to identify the nationwide prevalence of anaphylaxis and epinephrine prescription rates by age gro...
https://ift.tt/2IJoIz6
Reflection- and Distortion-Source Otoacoustic Emissions: Evidence for Increased Irregularity in the Human Cochlea During Aging
Abstract
Previous research on distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE) components has hinted at possible differences in the effect of aging on the two basic types of OAEs: those generated by a reflection mechanism in the cochlea and those created by nonlinear distortion (Abdala and Dhar in J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 13:403–421, 2012). This initial work led to the hypothesis that micromechanical irregularity ("roughness") increases in the aging cochlea, perhaps as the result of natural tissue degradation. Increased roughness would boost the backscattering of traveling waves (i.e., reflection emissions) while minimally impacting DPOAEs. To study the relational effect of aging on both types of emissions and address our hypothesis of its origin, we measured reflection- and distortion-type OAEs in 77 human subjects aged 18–76 years. The stimulus-frequency OAE (SFOAE), a reflection emission, and the distortion component of the DPOAE, a nonlinear distortion emission, were recorded at multiple stimulus levels across a four-octave range in all ears. Although the levels of both OAE types decreased with age, the rate of decline in OAE level was consistently greater for DPOAEs than for SFOAEs; that is, SFOAEs are relatively preserved with advancing age. Multiple regression analyses and other controls indicate that aging per se, and not hearing loss, drives this effect. Furthermore, SFOAE generation was simulated using computational modeling to explore the origin of this result. Increasing the amount of mechanical irregularity with age produced an enhancement of SFOAE levels, providing support for the hypothesis that increased intra-cochlear roughness during aging may preserve SFOAE levels. The characteristic aging effect—relatively preserved reflection-emission levels combined with more markedly reduced distortion-emission levels—indicates that SFOAE magnitudes in elderly individuals depend on more than simply the gain of the cochlear amplifier. This relative pattern of OAE decline with age may provide a diagnostic marker for aging-related changes in the cochlea.
https://ift.tt/2lPPYTo
Health-Related Quality of Life of Community Thyroid Cancer Survivors in Hangzhou, China
Thyroid, Ahead of Print.
https://ift.tt/2NhsdQI
Mid- to Late-Life Increases in Marker of Chronic Inflammation Tied to Dementia
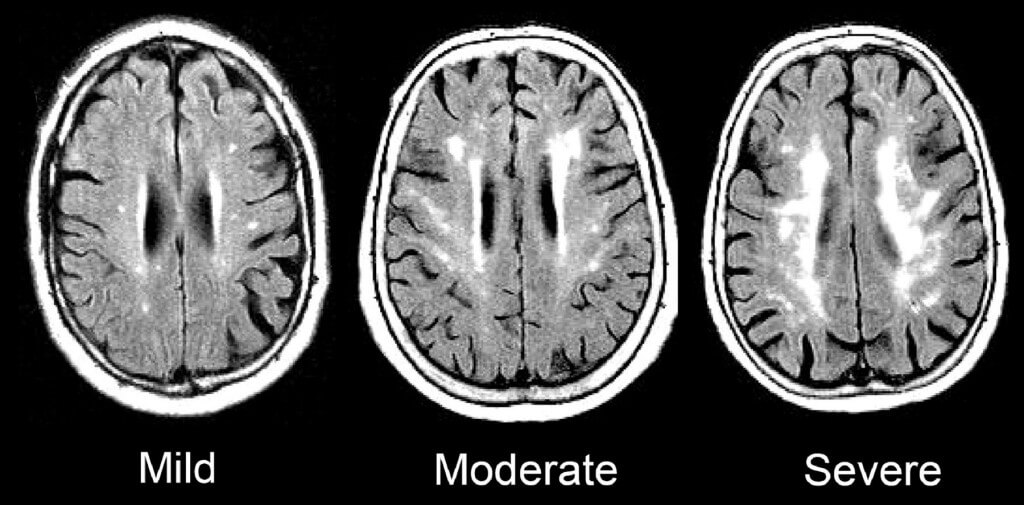
https://ift.tt/2NlcHTM
Objective measures of physical activity in patients with chronic unilateral vestibular hypofunction, and its relationship to handicap, anxiety and postural stability
Dizziness is one of the most common symptoms in the general population. Patients with dizziness experience balance problems and anxiety, which can lead to decreased physical activity levels and participation in their daily activities. Moreover, recovery of vestibular function from vestibular injury requires physical activity. Although there are reports that decreased physical activity is associated with handicap, anxiety, postural instability and reduced recovery of vestibular function in patients with chronic dizziness, these data were collected by self-report questionnaires.
https://ift.tt/2u2foRI
Experimental Drug Stops Parkinson’s Disease Progression in Mice
https://ift.tt/2z5wQug
Banana fruit: An “appealing” alternative for practicing suture techniques in resource-limited settings
Suturing is an important core surgical competency that requires continued practice. The purpose of this study was to evaluate bananas as a medium for practicing suture techniques in resource-limited settings.
https://ift.tt/2KBN3vI
Ixekizumab provides superior efficacy compared to ustekinumab over 52-weeks of treatment: results from IXORA-S, a phase 3 study
The IL-17 antagonist ixekizumab is effective in the clearance of plaque psoriasis. The superior efficacy of ixekizumab over ustekinumab observed at earlier time points is maintained through Week 52 and is associated with greater quality of life improvements. Over 52 weeks, the overall safety of ixekizumab and ustekinumab was comparable.
https://ift.tt/2IP3kZ8
Natural History of Disease Activity and Damage in Patients with Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
There are few longitudinal studies characterizing disease activity and damage of CLE patients. This study utilizes the CLASI to delineate the disease course of CLE patients on standard-of-care treatments. Having high baseline disease activity, minority race, or CLE disease duration <1 year predict CLE activity improvement.
https://ift.tt/2ILrmo6
Peripheral monocytes and neutrophils predict response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
We carried out a retrospective cohort study on patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC) to identify the peripheral blood count parameters associated with response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). There were 17 males and 15 females. Their median age was 64.5 years (range 20–84). History of smoking was present in 25/32 (78%) patients. Twelve patients received pembrolizumab, 19 patients nivolumab, and one patient nivolumab followed by pembrolizumab. Responses were observed in 19/32 (59%) patients, all partial responses. There was no difference in the distribution of sex, age, and smoking status between responders and non-responders. The median time to response (TTR) was 12 weeks (range 6–24) and the median duration of response (DoR) was 24 weeks (range 7–112). Higher pre-therapy absolute monocyte counts (AMCs) correlated to shorter TTR (p = 0.03), but not to response rate or DoR. Within the group of responders, those with AMCs > 700/mm3 had a significantly shorter median TTR than those with AMCs ≤ 700/mm3 (8 weeks vs 12 weeks; p = 0.048). Although baseline absolute neutrophil counts (ANCs) did not have any prognostic value, ANCs after first dose predicted response to ICI (p = 0.02). Patients with ANCs ≤ 4200/mm3 after first dose were more likely to respond than those with ANCs > 4200/mm3 (OR = 6.8; 95% CI 1.1–41.8; p = 0.05). Analysis of AMC and ANC before and during therapy may, therefore, provide an easy method to identify those mNSCLC patients most likely to benefit from ICI therapy.
https://ift.tt/2z1JvhD
Successful desensitization in a pediatric patient with acetazolamide allergy
Acetazolamide is an uncommon cause of IgE-mediated drug allergy. Classified as a sulfonamide, acetazolamide differs in chemical structure from sulfonamide antibiotics as it does not have an amine moiety at the N4 position. As a result, acetazolamide is infrequently a cause of IgE-mediated drug reactions and is less-likely to be cross-reactive in those with IgE-mediated allergy to sulfonamide antibiotics.1,2 Acetazolamide is reported to trigger non-IgE mediated reactions including pulmonary edema, delirium, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, and even Steven Johnsons syndrome.
https://ift.tt/2Kox2d7
Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy: diverse mechanisms of immune tolerance to allergens
Successful AIT induces establishment of long-term clinical tolerance against allergens resulting in reduction of symptoms and decrease in the need for pharmacotherapy, ultimately improving quality of life for patients suffering from IgE-mediated diseases.1
https://ift.tt/2KFQSg7
Health Literacy and Asthma Among Hispanic and African American Urban Adolescents with Undiagnosed Asthma
Asthma has high prevalence among adolescents, urban youth, and Hispanic and African American youth.1, 2 A large proportion of youth experience asthma symptoms, but are not diagnosed.3 Understanding more about undiagnosed asthma is an essential first step in increasing the likelihood of adolescents obtaining a diagnosis and treatment, and in preventing detrimental outcomes.
https://ift.tt/2KoMdTM
Specific-IgE to galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal) has limited utility in diagnosing meat allergy in a tick-endemic population
Sensitization to galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal) is considered a prerequisite to mammalian meat allergy (MMA), and can occur through tick bites, which is due to the paralysis tick, Ixodes holocyclus in Australia.1 The onset of symptoms is typically 3-6 hours following ingestion of mammalian meat, but immediate reactions are also described.2
https://ift.tt/2IKfpiq
Efficacy of C1Inhibitor concentrate in hereditary angioedema with C1Inhibitor deficiency: analysis in the French Cohort
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a rare genetic disease characterized by transitory recurrent subcutaneous and/or submucosal swelling episodes, which mainly affect skin, gastrointestinal tract and upper airways1. It should be divided into 2 forms according to the level of C1 inhibitor: HAE with C1 inhibitor deficiency (C1INH-HAE)1, and with a normal C1-Inhibitor level2, C1INH-HAE being the most frequent1. C1INH-HAE can be life-threatening especially when it affects upper airways3.
https://ift.tt/2Kt5kvS
Combo-VAS: an integrated outcome for assessing the perception of allergen immunotherapy effectiveness in clinical practice.
Allergen Immunotherapy (AIT) is at present indicated for treating respiratory, food, and venom allergy.1 Usually, AIT lasts for some years, but its efficacy is longstanding. These aspects make AIT irreplaceable compared to conventional pharmacological medications. However, AIT presents some disadvantages, including very long duration, high cost, potential side effects, and low compliance, mainly concerning the sublingual route.2 In addition, another limitation of AIT is the lack of simple and reliable criteria of efficacy assessment both considering clinical or laboratory biomarkers.
https://ift.tt/2KFoQl0
Mary Hewitt Loveless, MD, and the origin of venom immunotherapy
If ever there was an allergist whom I wish I had the chance to meet, it was Mary Hewitt Loveless, MD. Regrettably, I didn't, and so my sources for this remembrance are second-hand. Yet the legacy of this truly original investigator continues to grow, now 27 years after her death, at age 92, on June 2, 1991.
https://ift.tt/2KpxUOB
Chronic Tearing Induced by Apremilast
The therapeutic potential of Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE-4) inhibitors has been studied for various hyperproliferative skin disorders, such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. Inhibition of PDE-4 activity leads to elevated levels of intracellular cAMP; this results in anti-inflammatory effects in almost all inflammatory cells.1 Apremilast is an oral PDE-4 inhibitor that is FDA approved for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis in adults as well as patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. The most common adverse reactions to apremilast (≥5%) are diarrhea, nausea, headache, and upper respiratory tract infection.
https://ift.tt/2IKfnai
The T-win® technology: immune-modulating vaccines
Abstract
The T-win® technology is an innovative investigational approach designed to activate the body's endogenous anti-regulatory T cells (anti-Tregs) to target regulatory as well as malignant cells. Anti-Tregs are naturally occurring T cells that can directly react against regulatory immune cells because they recognize proteins that these targets express, including indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), tryptophan 2,6-dioxygenase, arginase, and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1). The T-win® technology is characterized by therapeutic vaccination with long peptide epitopes derived from these antigens and therefore offers a novel way to target genetically stable cells with regular human leukocyte antigen expression in the tumor microenvironment. The T-win® technology thus also represents a novel way to attract pro-inflammatory cells to the tumor microenvironment where they can directly affect immune inhibitory pathways, potentially altering tolerance to tumor antigens. The modification of an immune regulatory environment into a pro-inflammatory milieu potentiates effective anti-tumor T cell responses. Many regulatory immune cells may be reverted into effector cells given the right stimulus. Because T-win® technology is based on the immune-modulatory function of the vaccines, the vaccines activate both CD4 and CD8 anti-Tregs. Of importance, in clinical trials, vaccinations against IDO or PD-L1 to potentiate anti-Tregs have so far proved to be safe, with minimal toxicity.
https://ift.tt/2KFo6zo
Acquired resistance to cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
In recent times, advances in cancer immunotherapy have yielded impressive, durable clinical responses in patients with varied subtypes of cancer. However, a significant proportion of patients who initially demonstrate encouraging tumor regression develop resistance and progress over time. The identification of novel therapeutic approaches to overcome resistance may result in significantly improved clinical outcomes and remains an area of high scientific priority. This review aims to summarize the current knowledge regarding the role of both tumor-intrinsic and tumor-extrinsic factors in the development of resistance to cancer immunotherapy and to discuss current and possible future therapeutic strategies targeting these mechanisms.
https://ift.tt/2MJ4sjE
Gabapentin, Methadone, and Oxycodone With or Without Venlafaxine Hydrochloride in Managing Pain in Participants With Stage II-IV Squamous Cell Head and Neck Cancer Undergoing Chemoradiation Therapy
Interventions: Drug: Gabapentin; Drug: Methadone; Drug: Oxycodone; Other: Quality-of-Life Assessment; Other: Questionnaire Administration; Drug: Venlafaxine; Drug: Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Extended Release
Sponsors: Roswell Park Cancer Institute; National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Recruiting
https://ift.tt/2MFMiz6
Wearable Sensor for Biometrics During Locoregional Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer
Intervention: Device: wearable sensor
Sponsor: University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center
Recruiting
https://ift.tt/2KpbxsB
Sitravatinib (MGCD516) and Nivolumab in Oral Cavity Cancer Window Opportunity Study
Interventions: Drug: Sitravatinib; Biological: Nivolumab
Sponsors: University Health Network, Toronto; Mirati Therapeutics Inc.
Not yet recruiting
https://ift.tt/2MGV1ky
Nivolumab & IRX-2 With Surgery for Resectable Stage III-IVA Oral Cavity Cancer or HPV-Positive Oropharyngeal Cancer
Interventions: Drug: Cyclophosphamide; Biological: IRX-2; Biological: Nivolumab; Procedure: Surgery
Sponsors: Emory University; Bristol-Myers Squibb; IRX Therapeutics
Not yet recruiting
https://ift.tt/2Ko15BP
TPF Induction Chemotherapy vs PF Adjuvant Chemotherapy Combined With Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy in the Treatment of Locally Advanced NPC
Interventions: Drug: TPF+CCRT; Drug: CCRT+PF
Sponsor: Guiyang Medical University
Recruiting
https://ift.tt/2MH8FEo
Computer Algorithm Maps Cancer Resistance to Drugs, Therapy
https://ift.tt/2NiRQ3O
mTOR-mediated glycolysis contributes to the enhanced suppressive function of murine tumor-infiltrating monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells
Abstract
Immune cell activation occurs concurrently with metabolic reprogramming. As important components of the tumor microenvironment, monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (M-MDSCs) are featured by their potent immunosuppressive abilities on anti-tumor effector cells. However, little is known about the contribution of metabolic adaptations to their suppressive roles. In this study, we found that tumor-infiltrating M-MDSCs had the same phenotype with splenic M-MDSCs. Compared with splenic M-MDSCs, tumor-infiltrating M-MDSCs exhibited stronger suppressive activities which was accompanied by higher glycolysis. Inhibition of glycolysis impaired the suppressive function of tumor M-MDSCs. Meanwhile, the results demonstrated that mTOR was responsible for this function regulation. mTOR inhibition by rapamycin decreased the glycolysis and reduced the suppressive activities of these cells. Furthermore, rapamycin treatment inhibited the tumor growth and reduced the percentage of M-MDSCs in 3LL tumor bearing mice. These results demonstrated that modulation of metabolism in immune cells can be an effective way to enhance anti-tumor effects.
https://ift.tt/2KCyzIQ
Making a Difference by Addressing Social Determinants of Health
"Social Determinants of Health (SDH) are the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age, and the waiter set of forces and systems shaping the conditions of daily life. These forces and systems include economic policies and systems, development agendas, Social norms, social policies and political systems."1
SDH have a profound impact on our patients. "[T]hey are violent because they cause injury to people…. [C]linicians are not trained to understand such social forces, nor are we trained to alter them. Yet it has long been clear that many medical and public health interventions will fail if we are unable to understand the social determinants of disease."2 These determinants can be addressed at many different levels, helpfully classified as upstream, midstream, and downstream (Figure 1). Downstream determinants after temporally and spatially close to health efffects, upstream determinants are fundamental causes that set in motion causal pathways leading to health effects.3

In the case, "Childhood obesity in Mexico: social determinants of health and other risk factors" by Rodriguez et al, the most obvious aspects are the downstream effects of social determinants of health. A child is diagnosed with gastro-oesophageal reflux (GORD) and obesity. The downstream social determinants are the obvious presentation, and the first priority of the treating clinician. In this case, that can be seen with the lifestyle modifications recommended including changes in diet, exercise and sleeping habits and pharmacological treatment. As noted, these interventions were not very effective, and "The aim of this case report is to demonstrate how childhood obesity is rooted since pregnancy… and how the social determinants of health, like unsafe outdoor conditions, lack of infrastructure to exercise and suboptimal physical activity curriculum in government schools strongly influence the development and maintenance of childhood obesity and complicate management." (Figure 2)

The midstream effects are also easily seen. Regarding the physical environment, "the family avoids going to the park because of the unsafe outdoor and poor park conditions…. This family lives in a small apartment with a small patio (3x4m), so how much can the patient effectively exercise?" The case is no better when it comes to health behavior, "[T]he total daily caloric intake surpassed her daily caloric requirements by approximately 500 kcal/day…. [And] [i]n the case of our patient, 5 hours of screen use per day clearly exceed the recommended daily screen use hours…which affects the duration of sleep and contribute to the patient's sedentary lifestyle."
Finally, the upstream SDH are evident in the "suboptimal physical activity curriculum in government schools." The authors also note that "[M]ost community parks have been built in popular areas that are located far away from the most vulnerable." The authors also mention the social inequalities, "Women and children in low socioeconomic groups are the most vulnerable…. [B]eing a lower middle class family in Mexico and the inequalities this implies clearly affects management."
According to the WHO, "Obesity prevention and treatment requires a whole-of-government approach in which policies across all sectors systematically take health into account, avoid harmful health impacts, and thus improve population health and health equity."4 As clinicians, we see the full weight of SDH on the health of individuals. It is our duty and privilege to report on the harmful effects of policies and infrastructure that wreak havoc on the lives of the vulnerable. Healthcare professionals see the weakest at their most vulnerable, and the authors of this case are examples in not only reporting the facts but offering interventions. In their "Learning points" they include, "Schools must offer more than 60 min of physical activity per week to achieve a negative caloric balance in children. Construction of new parks in vulnerable neighborhoods and tackling crime are priorities to promote outdoor physical activity in Mexico."
BMJ Case Reports invites authors to submit global health case reports that describe the effects of SDH on vulnerable patients and ways to mitigate these effects. These cases could focus on:
- Upstream and midstream interventions and their impact on individual lives
- Downstream effects of SDH on individual patients
- Challenges to instituting SDH interventions as a healthcare professional
Manuscripts may be submitted by students, physicians, nurses and allied health professionals to BMJ Case Reports at www.bmjcasereports.com. For more information, review our guidance on how to write a global health case report and look through our online collection
To read more about SDH at BMJ Case Reports, please review:
- Ethiopian-Israeli community
- Social determinants of health: poverty, national infrastructure and investment
- Global health challenges in treating an elderly institutionalised patient: an oral medicine perspective
- A Rohingya refugee's journey in Australia and the barriers to accessing healthcare
To read more about SDH, please review:
[1] World Health Organization. Social determinants of health. What are social determinants of health [internet] available from http://www.who.int/social_determinants/en/ accessed 6/26/2018
[2] Farmer PE, Nizeye B, Stulac S, Keshavjee. Structural violence and clinical medicine. PLoS Med (2006) 3(10):e449
[3] BMJ Case Reports Global Health Curriculum (Available at casereports.BMJ.com/site/about/Global_health_curriculum_slides.pptx
[4] World Health Organization. Report of the commission on ending childhood obesity. World Health Organization; 2016. Geneva, Switzerland
The post Making a Difference by Addressing Social Determinants of Health appeared first on BMJ Case Reports blog.
https://ift.tt/2tVOJWp
Sinus computed tomography predicts clinical response to corticosteroids in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) is a heterogeneous inflammatory disease usually characterized by chronic eosinophilia in the sinonasal mucosa, which often requires glucocorticoid (GC) therapy...
https://ift.tt/2KEmenm
Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia (epithelioid hemangioma) of the external auditory canal, an unusual presentation in an adult female: a case report

https://ift.tt/2KEp7Ys
Complete small bowel obstruction without intussusception due to a submucosal lipoma

https://ift.tt/2MDXts0
Gallstone ileus 1 year after cholecystectomy

https://ift.tt/2KslCVG
